Disk Array FC60 User's Guide (A5635A)
Table Of Contents
- 1 Product Description
- 2 Array Planning
- 3 Installation
- 4 Managing the Disk Array
- 5 Troubleshooting
- 6 Removal and Replacement
- 7 Reference / Legal / Regulatory
'LVN$UUD\+LJK$YDLODELOLW\)HDWXUHV 45
Product Description
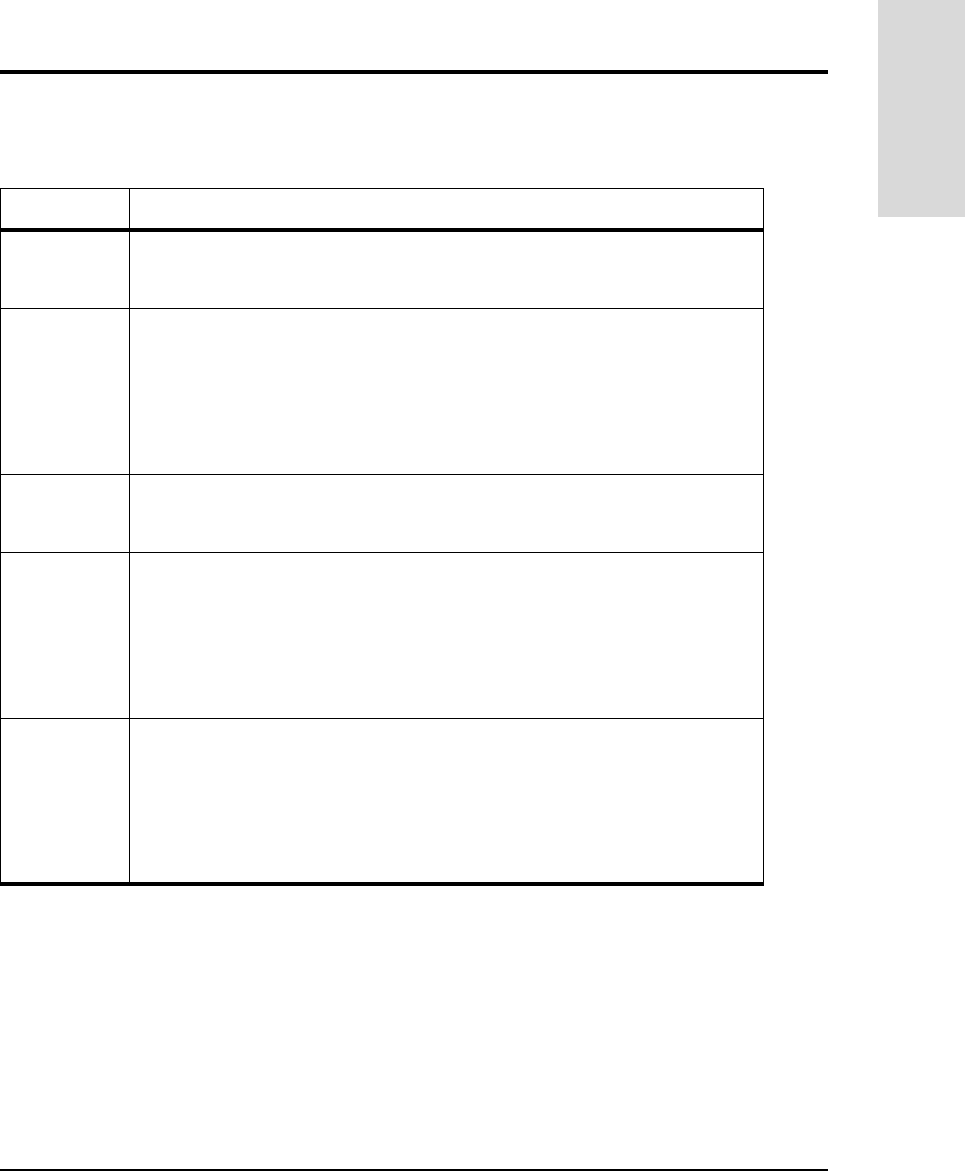
7DEOH
5$,'/HYHO&RPSDULVRQ*HQHUDO3HUIRUPDQFH&KDUDFWHULVWLFV
RAID Level General Performance Characteristics
RAID 0 – Simultaneous access to multiple disks increases I/O performance. In
general, the greater the number of mirrored pairs, the greater the increase
in performance.
RAID 1 – A RAID 1 mirrored pair requires one I/O operation for a read and two I/O
operations for a write, one to each disk in the pair.
– The disks in a RAID 1 mirrored pair are locked in synchronization, but the
disk array can read data from the module whose read/write heads are the
closest.
– RAID 1 read performance can be twice that of an individual disk. Write
performance can be the same as that of an individual disk.
RAID 0/1 – Simultaneous access to multiple mirrored pairs increases I/O performance.
In general, the greater the number of mirrored pairs, the greater the
increase in performance.
RAID 3 – Provides high read throughput for large sequential I/Os.
– Write performance is limited by the need to perform four I/O operations per
write request.
– Because some I/O operations occur simultaneously, performance depends
on the number of disks in the volume group. Additional disks may improve
performance.
– The I/O performance of RAID 5 benefits significantly from write caching.
RAID 5 – Provides high read throughput for small block-size requests (2 KB to 8 KB).
– Write performance is limited by the need to perform four I/O operations per
write request.
– Because some I/O operations occur simultaneously, performance depends
on the number of disks in the volume group. Additional disks may improve
performance.
– The I/O performance of RAID 5 benefits significantly from write caching.










