AB291A Fabric Clustering System Support Guide (12-port Switch), April 2004
Table Of Contents
- About This Document
- 1 Introduction to Technology
- 2 Hardware Overview
- 3 Installation Planning
- 4 Installing HP Fabric Clustering System
- 5 Administration and Management
- HP-UX Host Administration and Management
- Switch Administration and Management
- CLI Overview
- Using the CLI
- Advanced Switch Setup
- Configuration, Image, and Log Files
- Configuration, Image, and Log File Overview
- File Management
- Listing Configuration, Image, and Log Files
- Viewing Configuration Files
- Viewing Log Files
- Saving Configuration Files
- Saving for System Reboot
- Saving the Backup Configuration
- Specifying the Configuration to Use at
- Saving and Copying Files
- Downloading Files to the System
- Deleting Configuration, Image, and Log Files
- Managing Log Files
- Understanding the Log Format
- Uploading Log Files
- Administering the System
- 6 Monitoring and Troubleshooting
- A Specifications
- B HP 12-Port 4X Fabric Copper Switch Commands
- Show Commands
- show arp ethernet
- show arp IB
- show authentication
- show backplane
- show boot-config
- show card
- show card-inventory
- show clock
- show config
- show fan
- show host
- show ib
- show ib sm configuration
- show ib sm multicast
- show ib sm neighbor
- show ib sm node subnet-prefix
- show ib sm partition
- show ib sm port
- show ib sm service
- show ib sm switch
- show ib-agent channel-adapter
- show ib-agent summary
- show ib-agent switch
- show ib-agent switch linear-frd-info
- show ib-agent switch all mcast-info lid
- show ib-agent switch all node-info
- show ib-agent switch all pkey-info
- show ib-agent switch port-info
- show ib-agent switch sl-vl-map
- show ib-agent switch switch-info
- show interface ib
- show interface ib sm
- show interface ib sm statistics
- show interface mgmt-ethernet
- show interface mgmt-ib
- show interface mgmt-serial
- show ip
- show location
- show logging
- show ntp
- show power-supply
- show running-status
- show sensor
- show snmp
- show system-services
- show terminal
- show trace
- show user
- show version
- IP Commands
- HP Fabric Clustering System Commands
- Administrative Commands
- action
- boot-config
- broadcast
- card
- clock
- configure
- copy
- delete
- dir
- disable
- enable
- exec
- exit
- ftp-server enable
- gateway
- help
- history
- hostname
- install
- interface
- interface mgmt-ethernet
- interface mgmt-ib
- ip
- location
- login
- logging
- logout
- more
- ntp
- ping
- radius-server
- reload
- shutdown
- snmp-server
- telnet
- terminal length
- terminal time-out
- trace
- type
- username
- who
- write
- Show Commands
- C How to Use Windows HyperTerminal
- Glossary
HP 12-Port 4X Fabric Copper Switch Commands
Administrative Commands
Appendix B
287
Usage Guidelines:
The username command is used to:
Create and remove user accounts. The default CLI user accounts are guest, admin, and super.
Change user password. A user with read-write access may change their own password.
Assign access levels based upon functional areas, such as Fibre Channel, Ethernet, and HP Fabric Clustering
System administrative areas. Access levels may be unrestricted or read-only or read-write for the various
administrative areas. Unrestricted is the equivalent to the superuser.
Enable or disable the account.
Associate user accounts with SNMP community strings. This community string is also used as the password
for Element Manager access (Element Manager GUI is not supported in initial release of HP Fabric
Clustering System).
The user account must be created using the password argument before any other user configuration is
allowed.
The default unrestricted username for the CLI is super and the default password is super. SNMP community
strings provide the user credentials necessary to access Management Information Base (MIB) objects. The
default community-string assigned to the unrestricted user for the Element Manager is secret (Element
Manager GUI is not supported in initial release of HP Fabric Clustering System).
One unique community string is associated with each username and password. Community strings can be
associated with a variety of privilege levels. The user must have an SNMP community string to begin an
Element Manager session. If you do not want users to have SNMP access to the system, do not assign them a
community string. By default, a new user account has a null or empty community string. Only the
unrestricted user may view community strings (Element Manager GUI is not supported in initial release of
HP Fabric Clustering System).
Also, SNMP community strings are sent across the network in UDP packets. There is no encryption.
By default, new user accounts have read-only access. You may grant write privileges to a user for functional
areas, such as InfiniBand. The privileges are:
• ib-ro (InfiniBand read-only access)
• ib-rw (InfiniBand read-write)
• unrestricted-rw (Read-write access to all network configuration commands).
Privileges are order-dependent. You must enter multiple access privileges in the order shown in the list above.
When changing the privileges of an existing user, specify all the privileges allowed to the user (including
re-entering existing privileges), because the privilege argument removes all existing privileges and replaces
them with them with the new ones.
For security purposes, since multiple users exist on the system, it is highly recommended that you change the
default passwords after initial configuration. The default user accounts are listed in the table below.
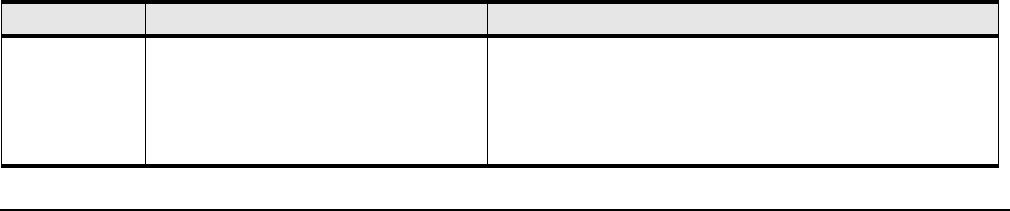
Table B-77 Default User Accounts
User Name Password Privilege
super By default, the password is “super”. The
default community string is “secret”.
The super user has unrestricted privileges. Use this account to
manage any part of the system. This user may view and modify
a configuration, as well as administer user accounts and access
privileges. This user configures the console and management
ports for initial chassis setup.










