AB291A Fabric Clustering System Support Guide (12-port Switch), April 2004
Table Of Contents
- About This Document
- 1 Introduction to Technology
- 2 Hardware Overview
- 3 Installation Planning
- 4 Installing HP Fabric Clustering System
- 5 Administration and Management
- HP-UX Host Administration and Management
- Switch Administration and Management
- CLI Overview
- Using the CLI
- Advanced Switch Setup
- Configuration, Image, and Log Files
- Configuration, Image, and Log File Overview
- File Management
- Listing Configuration, Image, and Log Files
- Viewing Configuration Files
- Viewing Log Files
- Saving Configuration Files
- Saving for System Reboot
- Saving the Backup Configuration
- Specifying the Configuration to Use at
- Saving and Copying Files
- Downloading Files to the System
- Deleting Configuration, Image, and Log Files
- Managing Log Files
- Understanding the Log Format
- Uploading Log Files
- Administering the System
- 6 Monitoring and Troubleshooting
- A Specifications
- B HP 12-Port 4X Fabric Copper Switch Commands
- Show Commands
- show arp ethernet
- show arp IB
- show authentication
- show backplane
- show boot-config
- show card
- show card-inventory
- show clock
- show config
- show fan
- show host
- show ib
- show ib sm configuration
- show ib sm multicast
- show ib sm neighbor
- show ib sm node subnet-prefix
- show ib sm partition
- show ib sm port
- show ib sm service
- show ib sm switch
- show ib-agent channel-adapter
- show ib-agent summary
- show ib-agent switch
- show ib-agent switch linear-frd-info
- show ib-agent switch all mcast-info lid
- show ib-agent switch all node-info
- show ib-agent switch all pkey-info
- show ib-agent switch port-info
- show ib-agent switch sl-vl-map
- show ib-agent switch switch-info
- show interface ib
- show interface ib sm
- show interface ib sm statistics
- show interface mgmt-ethernet
- show interface mgmt-ib
- show interface mgmt-serial
- show ip
- show location
- show logging
- show ntp
- show power-supply
- show running-status
- show sensor
- show snmp
- show system-services
- show terminal
- show trace
- show user
- show version
- IP Commands
- HP Fabric Clustering System Commands
- Administrative Commands
- action
- boot-config
- broadcast
- card
- clock
- configure
- copy
- delete
- dir
- disable
- enable
- exec
- exit
- ftp-server enable
- gateway
- help
- history
- hostname
- install
- interface
- interface mgmt-ethernet
- interface mgmt-ib
- ip
- location
- login
- logging
- logout
- more
- ntp
- ping
- radius-server
- reload
- shutdown
- snmp-server
- telnet
- terminal length
- terminal time-out
- trace
- type
- username
- who
- write
- Show Commands
- C How to Use Windows HyperTerminal
- Glossary
Chapter 5
Administration and Management
Switch Administration and Management
65
HP-IB(config)# in? <-- display all keywords that start with “in”
interface <-- only 1 keyword starts with “in”
HP-IB(config)# in ? <-- display the arguments to “interface”
ethernet - Configure Ethernet interfaces
fc - Configure Fibre Channel interfaces
gateway - Configure Gateway settings
ib - Configure InfiniBand interfaces
mgmt-ethernet - Configure Ethernet Management port
mgmt-ib - Configure Infiniband Management port
HP-IB(config)# in <-- waits for you to complete the “interface”
command string
After displaying the help information, the system enters the command string up to the question mark on the
input line and waits for you to complete the string. You do not have to retype the string.
If there is no space between a partially-entered command string and the question mark, a list of possible
completions are displayed, as shown above.
When enough characters have been entered to uniquely identify a command or keyword in a command string,
you may leave it as-is, enter a space, and then add additional keywords or arguments, or you can press the
<Tab> key to complete the commands or keywords to improve readability.
Command-Line Editing
Command-line editing is used to modify a command line you have just entered or a command line that had
been entered previously in the current CLI session. Command strings are displayed on the command line
when you:
• enter the strings manually
•use quick-help
• scroll through the command history
The CLI supports a variety of ways to move about and edit the currently displayed command line. These are
listed in the table below.
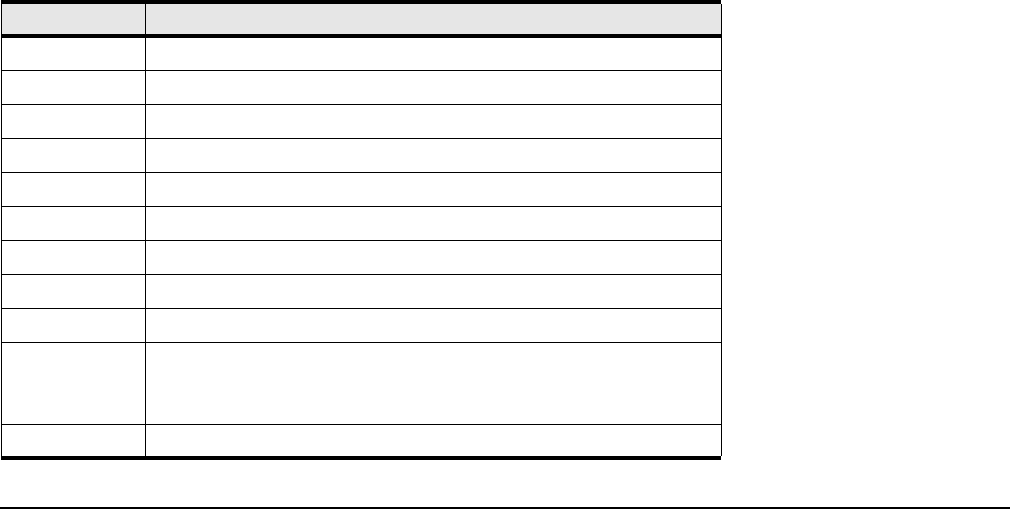
Table 5-4 Key Stroke Shortcuts
key description
<Ctrl>a Move to beginning of line.
<Ctrl>b Move cursor left one character.
<Ctrl>d Delete current character.
<Ctrl>e Move to end of line.
<Ctrl>f Move cursor right one character.
<Ctrl>k Delete from cursor to the end of the line.
<Ctrl>l Refresh input line.
<Ctrl>n Get next command from history.
<Ctrl>p Get previous command from history.
<Ctrl>q Return to use-execute mode. If a command is currently entered on the
command line, execute the command before returning to user-execute
mode.
<Ctrl>t Transpose current and previous character.










