AB291A Fabric Clustering System Support Guide (12-port Switch), April 2004
Table Of Contents
- About This Document
- 1 Introduction to Technology
- 2 Hardware Overview
- 3 Installation Planning
- 4 Installing HP Fabric Clustering System
- 5 Administration and Management
- HP-UX Host Administration and Management
- Switch Administration and Management
- CLI Overview
- Using the CLI
- Advanced Switch Setup
- Configuration, Image, and Log Files
- Configuration, Image, and Log File Overview
- File Management
- Listing Configuration, Image, and Log Files
- Viewing Configuration Files
- Viewing Log Files
- Saving Configuration Files
- Saving for System Reboot
- Saving the Backup Configuration
- Specifying the Configuration to Use at
- Saving and Copying Files
- Downloading Files to the System
- Deleting Configuration, Image, and Log Files
- Managing Log Files
- Understanding the Log Format
- Uploading Log Files
- Administering the System
- 6 Monitoring and Troubleshooting
- A Specifications
- B HP 12-Port 4X Fabric Copper Switch Commands
- Show Commands
- show arp ethernet
- show arp IB
- show authentication
- show backplane
- show boot-config
- show card
- show card-inventory
- show clock
- show config
- show fan
- show host
- show ib
- show ib sm configuration
- show ib sm multicast
- show ib sm neighbor
- show ib sm node subnet-prefix
- show ib sm partition
- show ib sm port
- show ib sm service
- show ib sm switch
- show ib-agent channel-adapter
- show ib-agent summary
- show ib-agent switch
- show ib-agent switch linear-frd-info
- show ib-agent switch all mcast-info lid
- show ib-agent switch all node-info
- show ib-agent switch all pkey-info
- show ib-agent switch port-info
- show ib-agent switch sl-vl-map
- show ib-agent switch switch-info
- show interface ib
- show interface ib sm
- show interface ib sm statistics
- show interface mgmt-ethernet
- show interface mgmt-ib
- show interface mgmt-serial
- show ip
- show location
- show logging
- show ntp
- show power-supply
- show running-status
- show sensor
- show snmp
- show system-services
- show terminal
- show trace
- show user
- show version
- IP Commands
- HP Fabric Clustering System Commands
- Administrative Commands
- action
- boot-config
- broadcast
- card
- clock
- configure
- copy
- delete
- dir
- disable
- enable
- exec
- exit
- ftp-server enable
- gateway
- help
- history
- hostname
- install
- interface
- interface mgmt-ethernet
- interface mgmt-ib
- ip
- location
- login
- logging
- logout
- more
- ntp
- ping
- radius-server
- reload
- shutdown
- snmp-server
- telnet
- terminal length
- terminal time-out
- trace
- type
- username
- who
- write
- Show Commands
- C How to Use Windows HyperTerminal
- Glossary
Chapter 5
Administration and Management
Switch Administration and Management
90
last-login : Thu Oct 10 09:13:10 2002
last-unsuccessful-login : Thu Oct 10 09:12:32 2002
HP-IB> write waldo "Connection to FC array 15 is now working."
HP-IB>
Creating User Accounts
About User Accounts A user account is used to control who gains access to the system. Access can be
achieved through the CLI (console, telnet, SSH) and SNMP. CLI access is authorized through a password
validation. SNMP access is authorized through a community-string validation.
User accounts can be added, deleted, and modified as needed. Up to 15 user accounts are supported. Only
user(s) that have the unrestricted ReadWrite permission level can add, delete, and modify user accounts.
Each system is preconfigured with 3 factory default user accounts.
Each user account can be administratively enabled and disabled as needed. The user can disable a user
account without having to delete it from the system.
Each user account is uniquely identified by an ascii string that can be up to 20 characters long. No two user
accounts can have the same user name.
In order for users to initiate an administration session, the User has to supply login credentials. The
credentials supplied depend upon the interface being used.
The access system associates the following key elements:
• Username - Creates a unique username in the system.
•Password
• Community String - Unique string used for the SNMP Network Managers.
• Privilege Level - Allows combinations of different privileges.
The CLI uses username and password. Granular access rights are given by privilege level.
Understanding Usernames and Passwords CLI users enter standard username and password
information to begin a CLI session. By default, you may log on as one of three users, super, admin, or guest.
The user names are shown in the table below.
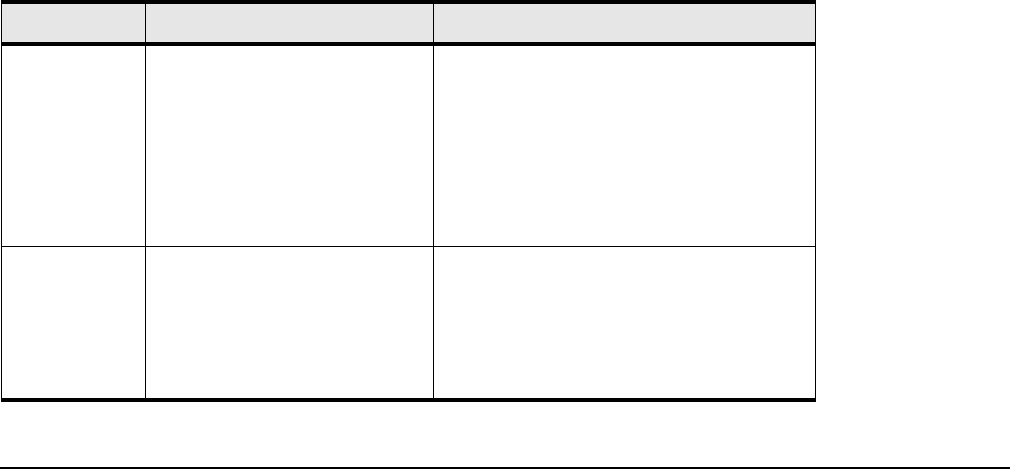
Table 5-7 Default User Names, Passwords and Privileges
User Name Passwords privileges
super By default, the password is
“super”. The default
community string is “secret”.
The super user has unrestricted
privileges. Use this account to manage
any part of the system. This user may
view and modify a configuration, as well
as administer user accounts and access
privileges. This user configures the
console and management ports for
initial chassis setup.
admin By default, the password is
“admin”. The default
community string is
“private”.
The admin user has general read-write
privileges. This user may view and
modify the current configuration.
However, the admin user can change
only its own user information, such as
the admin password.










