Converged networks with Fibre Channel over Ethernet and Data Center Bridging
Table Of Contents
9
frames of varying priority or TCs: If one queue becomes full, the device must send a pause frame to the
other side of the link. This pauses all traffic, regardless of TC/priority.
Supporting lossless behavior of block storage protocols on legacy Ethernet networks requires using legacy
pause frames. However, this forces all traffic to be lossless on that link. The most bursty or bandwidth driven
TCs dictate the behaviors of all TCs. Many types of traffic flows, for example real-time audio/video data
streams, don’t require lossless transmission and don’t perform well on a lossless link. Even traditional TCP-
based traffic flows optimized for lossy communications environments often don’t perform well in lossless
environments that transport different classes of traffic with vastly different characteristics simultaneously.
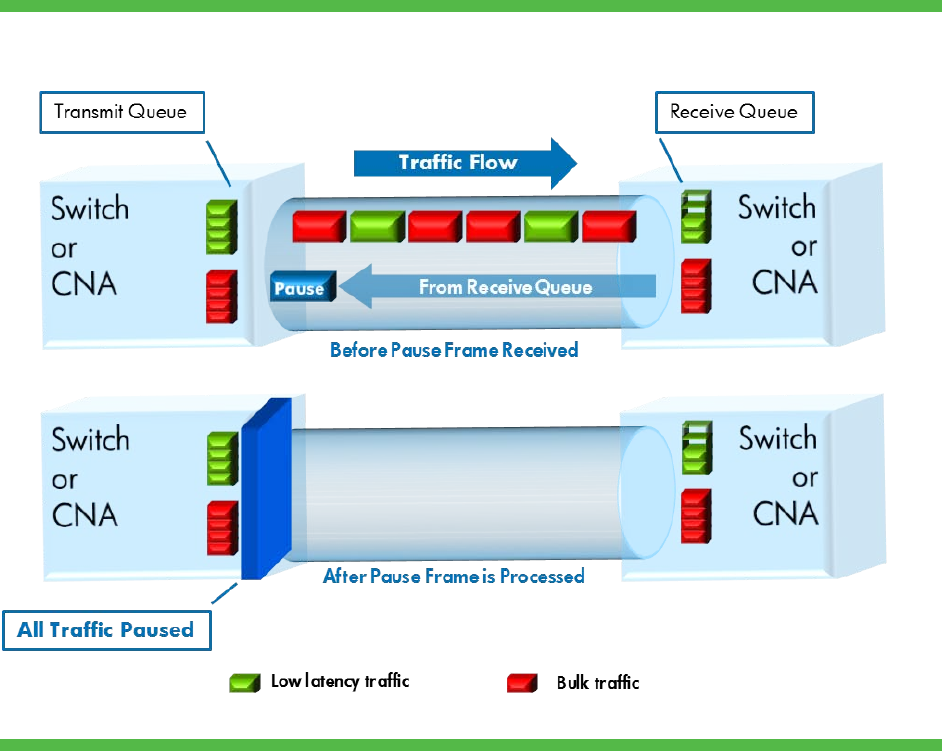
In Figure 5, low-bandwidth, latency-sensitive traffic for voice/video/financial transactions (green) and
higher bandwidth bulk traffic for storage (red) are sent on a link. The receiving device has two sets of
queues for receiving and storing data, one for green traffic and the other for red traffic. In this example, the
high bandwidth bulk traffic will fill the red receive queue. Although the green traffic has plenty of queue
space available, the receiving device sends a pause frame because the red queue is full. The transmitting
device receives this pause frame and stops all traffic on the link. Long delays interrupt the low latency
traffic.
Figure 5. Legacy pause-based flow control
Priority-based Flow Control (PFC) uses a modified version of the pause frame called a Per Priority Pause
(PPP) frame. PPP allows the pause frame to specify which priorities, and thus which TCs, to pause. PFC uses
the priority levels in the class of service fields of the 802.1Qbb PPP frame header. When a network device
has one or more receive queues that are nearly full, it constructs a PPP frame to send to the remote link
partner. The remote device examines the class of service fields to determine which priorities/TCs to pause.
The port’s transmit function will stop sending the priorities/TCs going to the full ingress queues on the
congested device without affecting priorities/TCs going to unfilled queues on the congested device.










