FCoE Cookbook for HP Virtual Connect Version 4.20 Firmware Enhancements May 2014
74
Benefits
Although the NPV mode can be intended to help address third-party interoperability issues in multivendor environment,
in large Cisco fabrics, the NPV mode can be used to simplify the switch configuration, the points of management and
also to better control the number of domain IDs to increase the SAN scalability as you can add switches to the faric
without adding more domain IDs but the number of ports to the fabric are increased.
In NPV mode, fabric logins are passed upstream from the edge switch to the core MDS switch, this eliminates the need to
configure unique domain ID and Zoning. The Nexus acts as a pass through switch and converts the Fabric Login (FLOGI)
command to a Fabric Discovery (FDISC) command and passes it to the upstream SAN switch.
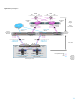
The use of multiple FCoE uplink ports on each VC module connected to Nexus allows dynamically distribution of the FCoE
traffic across the ports using a round robin format.
By providing ability to define multiple FCoE VLANs on a single set of uplinks, VC allows multi-VSAN capability to be
enabled on the Nexus NPV switches and Cisco’s MDS. VSANs allow an enterprise customer to maintain single physical
SAN infrastructure, while providing separation and traffic isolation to the servers based on the business unit, types of
the operating systems or need for logical isolation. Servers can therefore access to a different VSANs and connect to
storage targets located in different logical SAN environment.
F-Port Port Channeling with VSAN trunking, fully supported under the NPV mode, is also used between the Nexus and
MDS core switches to increase the high availability and to create enough SAN subscription.
Considerations
In NPV mode, the switch does not operate as a typical Fibre Channel switch, fabric services (i.e. Name Service, Fabric
Login, zoning, etc.) are not available and Fibre Channel switching is not performed: all traffic is switched upstream in the
core switch.
The NPV mode uses N Port ID Virtualization (NPIV) technology, F_Ports that normally connect to the fabric are
configured in this mode as NP_Ports and use NPIV to register multiple WWPNs to the F_Port on the other end.
Note: To convert a switch into NPV mode, you set the NPV feature to enable. This configuration command automatically
triggers a switch reboot and the system configuration is erased. You cannot configure NPV mode on a per-interface
basis. NPV mode applies to the entire switch.
For more information about the NPV Mode and Cisco support, see
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/switches/datacenter/nexus5000/sw/configuration/guide/cli/npv.html
Multiple VSAN support
The number of FCoE networks per Shared Uplink Set is limited to 32. The number of FCoE networks is additionally
limited by the 1000 network domain limit.
For this feature to successfully integrate with Cisco Nexus switches it is important to note that for each FCoE VLAN a
unique FC VSAN must be created and association between the two must be strictly configured as 1-to-1. Mapping of a
single VLAN into multiple VSANs is not supported. This requirement is documented in Cisco’s best practice
recommendations.
All of the FCoE networks will share the same lossless Priority Flow Control (PFC) queue on any specific shared uplink set.
Sharing PFC queue between multiple VSANs will make it possible that traffic from one VSAN may have impact on traffic
from other VSANs. For that reason, it is highly recommended to create enough SAN subscription (i.e. by using a suitable
number of uplink between VC and Nexus but also between Nexus and Cisco MDS) to avoid any over-subscription issues
that would prevent SAN to pause and therefore to impact other VSANs. Therefore the use of a SAN Port Channel with
VSAN trunking between the Nexus and MDS switches is highly recommended.
SAN Port Channel and Trunking
The use of SAN Port Channel and VSAN trunking between the Nexus and MDS core switches are fully supported under the
NPV mode. F-Port Port Channeling increases the uplink resiliency, optimizes the bandwidth utilization and increases the
aggregated bandwidth with load balancing.
SAN Port Channel between Nexus and upstream switches is only supported with Cisco switches (MDS or Nexus series).
NP ports that are members of the same SAN Port Channel cannot be connected to different core switches.