- Hewlett-Packard Switch User Manual
Table Of Contents
- HP ProCurve 2520 Switches Management and Configuration Guide
- Front Cover
- Title Page
- Copyright, Notices, & Publication Data
- Contents
- Feature Index
- 1.Getting Started
- 2.Selecting a Management Interface
- 3.Using the Menu Interface
- 4.Using the Command Line Interface (CLI)
- 5.Using the ProCurve Web Browser Interface
- 6.Switch Memory and Configuration
- 7.Interface Access and System Information
- 8.Configuring IP Addressing
- 9.Time Protocols
- 10.Port Status and Configuration
- Contents
- Overview
- Viewing Port Status and Configuring Port Parameters
- Menu: Port Status and Configuration
- CLI: Viewing Port Status and Configuring Port Parameters
- Customizing the Show Interfaces Command
- Viewing Port Utilization Statistics
- Viewing Transceiver Status
- Enabling or Disabling Ports and Configuring Port Mode
- Enabling or Disabling Flow Control
- Configuring a Broadcast Limit on the Switch
- Configuring ProCurve Auto-MDIX
- Web: Viewing Port Status and Configuring Port Parameters
- Using Friendly (Optional) Port Names
- 11.Power Over Ethernet (PoE) Operation
- 12.Port Trunking
- Contents
- Overview
- Port Trunk Features and Operation
- Trunk Configuration Methods
- Menu: Viewing and Configuring a Static Trunk Group
- CLI: Viewing and Configuring Port Trunk Groups
- Web: Viewing Existing Port Trunk Groups
- Trunk Group Operation Using LACP
- Trunk Group Operation Using the “Trunk” Option
- How the Switch Lists Trunk Data
- Outbound Traffic Distribution Across Trunked Links
- 13.Configuring for Network Management Applications
- Contents
- Using SNMP Tools To Manage the Switch
- LLDP (Link-Layer Discovery Protocol)
- Terminology
- General LLDP Operation
- Packet Boundaries in a Network Topology
- Configuration Options
- Options for Reading LLDP Information Collected by the Switch
- LLDP and LLDP-MED Standards Compatibility
- LLDP Operating Rules
- Configuring LLDP Operation
- LLDP-MED (Media-Endpoint-Discovery)
- Displaying Advertisement Data
- LLDP Operating Notes
- LLDP and CDP Data Management
- A.File Transfers
- B.Monitoring and Analyzing Switch Operation
- Contents
- Overview
- Status and Counters Data
- Menu Access To Status and Counters
- General System Information
- Task Monitor—Collecting Processor Data
- Switch Management Address Information
- Port Status
- Viewing Port and Trunk Group Statistics and Flow Control Status
- Viewing the Switch’s MAC Address Tables
- Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP) Information
- Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) Status
- VLAN Information
- Web Browser Interface Status Information
- Interface Monitoring Features
- Locating a Device
- C.Troubleshooting
- Contents
- Overview
- Troubleshooting Approaches
- Browser or Telnet Access Problems
- Unusual Network Activity
- General Problems
- 802.1Q Prioritization Problems
- IGMP-Related Problems
- LACP-Related Problems
- Port-Based Access Control (802.1X)-Related Problems
- QoS-Related Problems
- Radius-Related Problems
- Spanning-Tree Protocol (MSTP) and Fast-Uplink Problems
- SSH-Related Problems
- TACACS-Related Problems
- TimeP, SNTP, or Gateway Problems
- VLAN-Related Problems
- Fan Failure
- Using the Event Log for Troubleshooting Switch Problems
- Debug/Syslog Operation
- Debug/Syslog Messaging
- Debug/Syslog Destination Devices
- Debug/Syslog Configuration Commands
- Configuring Debug/Syslog Operation
- Debug Command
- Logging Command
- Adding a Description for a Syslog Server
- Adding a Priority Description
- Configuring the Severity Level for Event Log Messages Sent to a Syslog Server
- Operating Notes for Debug and Syslog
- Diagnostic Tools
- Viewing Switch Configuration and Operation
- Restoring the Factory-Default Configuration
- Restoring a Flash Image
- DNS Resolver
- D.MAC Address Management
- E.Daylight Savings Time on ProCurve Switches
- F.Power-Saving Features
- Index
- Notices & Publication Data
Port Trunking
Trunk Configuration Methods
Spanning Tree: 802.1D (STP) and 802.1w (RSTP) Spanning Tree operate as a global setting on the switch (with one instance
of Spanning Tree per switch). 802.1s (MSTP) Spanning Tree operates on a per-instance basis (with multiple instances
allowed per switch). For each SpanningTree instance, you can adjust Spanning Tree parameters on a per-port basis. A
static trunk of any type appears in the Spanning Tree configuration display, and you can configure Spanning Tree
parameters for a static trunk in the same way that you would configure Spanning Tree parameters on a non-trunked port.
(Note that the switch lists the trunk by name—such as Trk1—and does not list the individual ports in the trunk.) For
example, if ports C1 and C2 are configured as a static trunk named Trk1, they are listed in the Spanning Tree display as
Trk1 and do not appear as individual ports in the Spanning Tree displays.
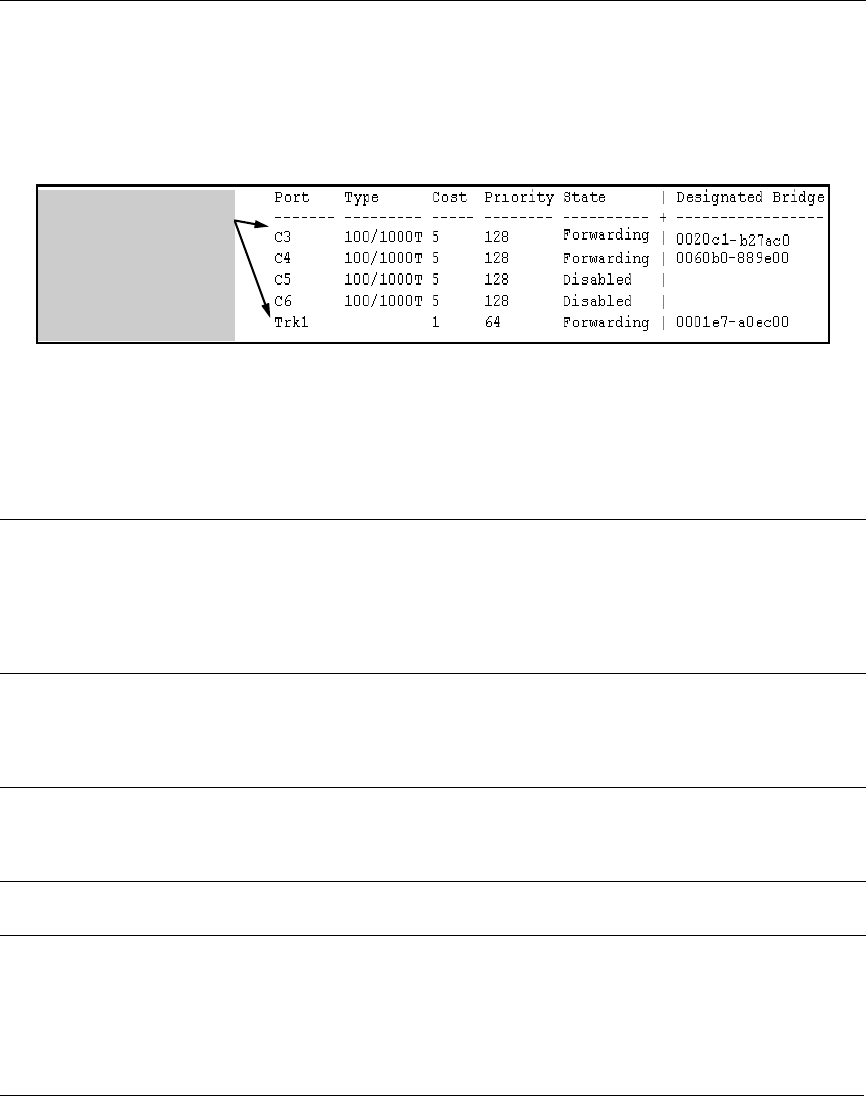
In this example showing
part of the show spanning-
tree listing, ports C1 and C2
are members of TRK1 and
do not appear as individual
ports in the port
configuration part of the
listing.
Figure 12-3. Example of a Port Trunk in a Spanning Tree Listing
When Spanning Tree forwards on a trunk, all ports in the trunk will be forwarding. Conversely, when Spanning Tree blocks
a trunk, all ports in the trunk are blocked.
Note: A dynamic LACP trunk operates only with the default Spanning Tree settings. Also, this type of trunk appears in
the CLI show spanning-tree display, but not in the Spanning Tree Operation display
of the Menu interface.
If you remove a port from a static trunk, the port retains the same Spanning Tree settings that were configured for the trunk.
IP Multicast Protocol (IGMP): A static trunk of any type appears in the IGMP configuration display, and you can configure
IGMP for a static trunk in the same way that you would configure IGMP on a non-trunked port. (Note that the switch lists
the trunk by name—such as Trk1—and does not list the individual ports in the trunk.) Also, creating a new trunk
automatically places the trunk in IGMP Auto status if IGMP is enabled for the default VLAN. A dynamic LACP trunk
operates only with the default IGMP settings and does not appear in the IGMP configuration display or
show ip igmp
listing.
VLANs: Creating a new trunk automatically places the trunk in the DEFAULT_VLAN, regardless of whether the ports in
the trunk were in another VLAN. Similarly, removing a port from a trunk group automatically places the port in the default
VLAN. You can configure a static trunk in the same way that you configure a port for membership in any VLAN.
Note: For a dynamic LACP trunk to operate in a VLAN other than the default VLAN (DEFAULT_VLAN), GVRP must be
enabled. Refer to “Trunk Group Operation Using LACP” on page 12-18.
Port Security: Trunk groups (and their individual ports) cannot be configured for port security, and the switch excludes
trunked ports from the
show port-security listing. If you configure non-default port security settings for a port, then
subsequently try to place the port in a trunk, you will see the following message and the command will not be executed:
< port-list > Command cannot operate over a logical port.
Monitor Port:
Note: A trunk cannot be a monitor port. A monitor port can monitor a static trunk but cannot monitor a dynamic LACP trunk.
12-8










