- Hewlett-Packard Switch User Manual
Table Of Contents
- HP ProCurve 2520 Switches Management and Configuration Guide
- Front Cover
- Title Page
- Copyright, Notices, & Publication Data
- Contents
- Feature Index
- 1.Getting Started
- 2.Selecting a Management Interface
- 3.Using the Menu Interface
- 4.Using the Command Line Interface (CLI)
- 5.Using the ProCurve Web Browser Interface
- 6.Switch Memory and Configuration
- 7.Interface Access and System Information
- 8.Configuring IP Addressing
- 9.Time Protocols
- 10.Port Status and Configuration
- Contents
- Overview
- Viewing Port Status and Configuring Port Parameters
- Menu: Port Status and Configuration
- CLI: Viewing Port Status and Configuring Port Parameters
- Customizing the Show Interfaces Command
- Viewing Port Utilization Statistics
- Viewing Transceiver Status
- Enabling or Disabling Ports and Configuring Port Mode
- Enabling or Disabling Flow Control
- Configuring a Broadcast Limit on the Switch
- Configuring ProCurve Auto-MDIX
- Web: Viewing Port Status and Configuring Port Parameters
- Using Friendly (Optional) Port Names
- 11.Power Over Ethernet (PoE) Operation
- 12.Port Trunking
- Contents
- Overview
- Port Trunk Features and Operation
- Trunk Configuration Methods
- Menu: Viewing and Configuring a Static Trunk Group
- CLI: Viewing and Configuring Port Trunk Groups
- Web: Viewing Existing Port Trunk Groups
- Trunk Group Operation Using LACP
- Trunk Group Operation Using the “Trunk” Option
- How the Switch Lists Trunk Data
- Outbound Traffic Distribution Across Trunked Links
- 13.Configuring for Network Management Applications
- Contents
- Using SNMP Tools To Manage the Switch
- LLDP (Link-Layer Discovery Protocol)
- Terminology
- General LLDP Operation
- Packet Boundaries in a Network Topology
- Configuration Options
- Options for Reading LLDP Information Collected by the Switch
- LLDP and LLDP-MED Standards Compatibility
- LLDP Operating Rules
- Configuring LLDP Operation
- LLDP-MED (Media-Endpoint-Discovery)
- Displaying Advertisement Data
- LLDP Operating Notes
- LLDP and CDP Data Management
- A.File Transfers
- B.Monitoring and Analyzing Switch Operation
- Contents
- Overview
- Status and Counters Data
- Menu Access To Status and Counters
- General System Information
- Task Monitor—Collecting Processor Data
- Switch Management Address Information
- Port Status
- Viewing Port and Trunk Group Statistics and Flow Control Status
- Viewing the Switch’s MAC Address Tables
- Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP) Information
- Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) Status
- VLAN Information
- Web Browser Interface Status Information
- Interface Monitoring Features
- Locating a Device
- C.Troubleshooting
- Contents
- Overview
- Troubleshooting Approaches
- Browser or Telnet Access Problems
- Unusual Network Activity
- General Problems
- 802.1Q Prioritization Problems
- IGMP-Related Problems
- LACP-Related Problems
- Port-Based Access Control (802.1X)-Related Problems
- QoS-Related Problems
- Radius-Related Problems
- Spanning-Tree Protocol (MSTP) and Fast-Uplink Problems
- SSH-Related Problems
- TACACS-Related Problems
- TimeP, SNTP, or Gateway Problems
- VLAN-Related Problems
- Fan Failure
- Using the Event Log for Troubleshooting Switch Problems
- Debug/Syslog Operation
- Debug/Syslog Messaging
- Debug/Syslog Destination Devices
- Debug/Syslog Configuration Commands
- Configuring Debug/Syslog Operation
- Debug Command
- Logging Command
- Adding a Description for a Syslog Server
- Adding a Priority Description
- Configuring the Severity Level for Event Log Messages Sent to a Syslog Server
- Operating Notes for Debug and Syslog
- Diagnostic Tools
- Viewing Switch Configuration and Operation
- Restoring the Factory-Default Configuration
- Restoring a Flash Image
- DNS Resolver
- D.MAC Address Management
- E.Daylight Savings Time on ProCurve Switches
- F.Power-Saving Features
- Index
- Notices & Publication Data
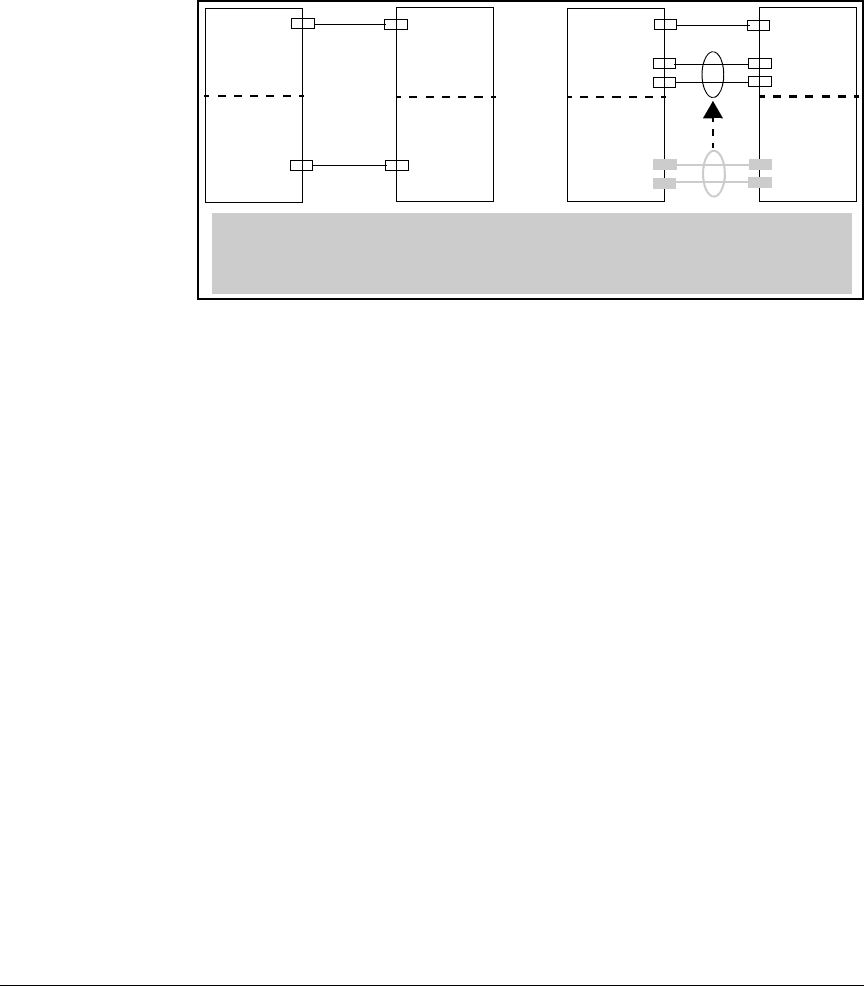
Port Trunking
Trunk Group Operation Using LACP
■ If there are ports that you do not want on the default VLAN, ensure that
they cannot become dynamic LACP trunk members. Otherwise a traffic
loop can unexpectedly occur. For example:
VLAN-1
(Default
VLAN)
VLAN-2
VLAN-1
(Default
VLAN)
VLAN-2
VLAN-1
(Default
VLAN)
VLAN-2
VLAN-1
(Default
VLAN)
VLAN-2
If the ports in VLAN 2 are configured to allow a dynamic trunk (and GVRP is disabled), adding a
second link in VLAN 2 automatically forms a dynamic LACP trunk and moves the trunk to VLAN-1
(the default VLAN), which creates a traffic loop in VLAN 1 between the two switches and
eliminates the link in VLAN 2 between the two switches.
Figure 12-12. A Dynamic LACP Trunk Forming in a VLAN Can Cause a Traffic Loop
Easy control methods include either disabling LACP on the selected ports or
configuring them to operate in static LACP trunks.
Spanning Tree and IGMP. If Spanning Tree and/or IGMP is enabled in the
switch, a dynamic LACP trunk operates only with the default settings for these
features and does not appear in the port listings for these features.
Half-Duplex and/or Different Port Speeds Not Allowed in LACP
Trunks. The ports on both sides of an LACP trunk must be configured for
the same speed and for full-duplex (FDx). The 802.3ad LACP standard speci-
fies a full-duplex (FDx) requirement for LACP trunking. (10-gigabit ports
operate only at FDx.)
A port configured as LACP passive and not assigned to a port trunk can be
configured to half-duplex (HDx). However, in any of the following cases, a
port cannot be reconfigured to an HDx setting:
■ If the port is a 10-gigabit port.
■ If a port is set to LACP Active, you cannot configure it to HDx.
■ If a port is already a member of a static or dynamic LACP trunk, you cannot
configure it to HDx.
■ If a port is already set to HDx, the switch does not allow you to configure
it for a static or dynamic LACP trunk.
12-25










