HP Insight Management WBEM Providers for HP integrated VMware ESXi 5.0 U1 June 2012 Profiles
WBEM TC Template
12 DMTF Confidential Version 0.9.1
implementation of profiles with their registration in the interop namespace and not to be normative with
respect to the specific profiles being illustrated. For example, HP or the DMTF may or may not extend or
implement the DMTF Fan profile in the manner shown in these diagrams.
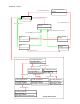
Figure 3 shows a simple implementation of a system containing one processor and one fan that have
been extended via HP extension profiles. The DMTF base server profile has also been extended via the
HP Base Server profile. The example uses the scoping class methodology for registering compliance to
profiles. Using the methodology only one CIM_ElementConformsToProfile is required to associate the
single autonomous profile (DMTF Base Server in this case) with the central class instance
(HP_ComputerSystem in this case) in the implementation namespace. Note that even though the
scoping class is of type HP_ComputerSystem, generic SMASH based clients would see an instance of
CIM_ComputerSystem because HP_ComputerSystem sub-classed off of CIM_ComputerSystem.
The interop namespace contains the same referenced profiles as you would expect given the description
contained in the Profile Registration Profile (DSP1033). The registered DMTF Base Server profile
references both the DMTF Fan and CPU registered profiles because the implementation namespace
contains implementations (or central classes) for each. In addition, the interop namespace contains the
registrations for extensions to the base model because the DMTF Base Server, CPU, and Fan profiles
have been extended with HP specific profiles (HP Base Server, HP CPU, and HP Fan). From the interop
namespace clients can tell which autonomous and component profiles are implemented and which of
those profiles have been extended via HP extension profiles.