64-bit Intel Xeon Processorwith 1MB L2 Cache Thermal/Mechanical Design Guidelines
Table Of Contents
R
Thermal/Mechanical Reference Design
64-bit Intel
®
Xeon™ Processor MP with 1 MB L2 Cache 17
Thermal/Mechanical Design Guidelines
Where:
Ψ
CS
= Thermal characterization parameter of the TIM (°C/W).
Ψ
SA
= Thermal characterization parameter from heatsink-to-local ambient (°C/W).
Ψ
CS
is strongly dependent on the thermal conductivity and thickness of the TIM between the
heatsink and IHS.
Ψ
SA
is a measure of the thermal characterization parameter from the bottom of the heatsink to the
local ambient air. Ψ
SA
is dependent on the heatsink material, thermal conductivity, and geometry. It
is also strongly dependent on the air velocity through the fins of the heatsink and the local ambient
temperature surrounding the heatsink.
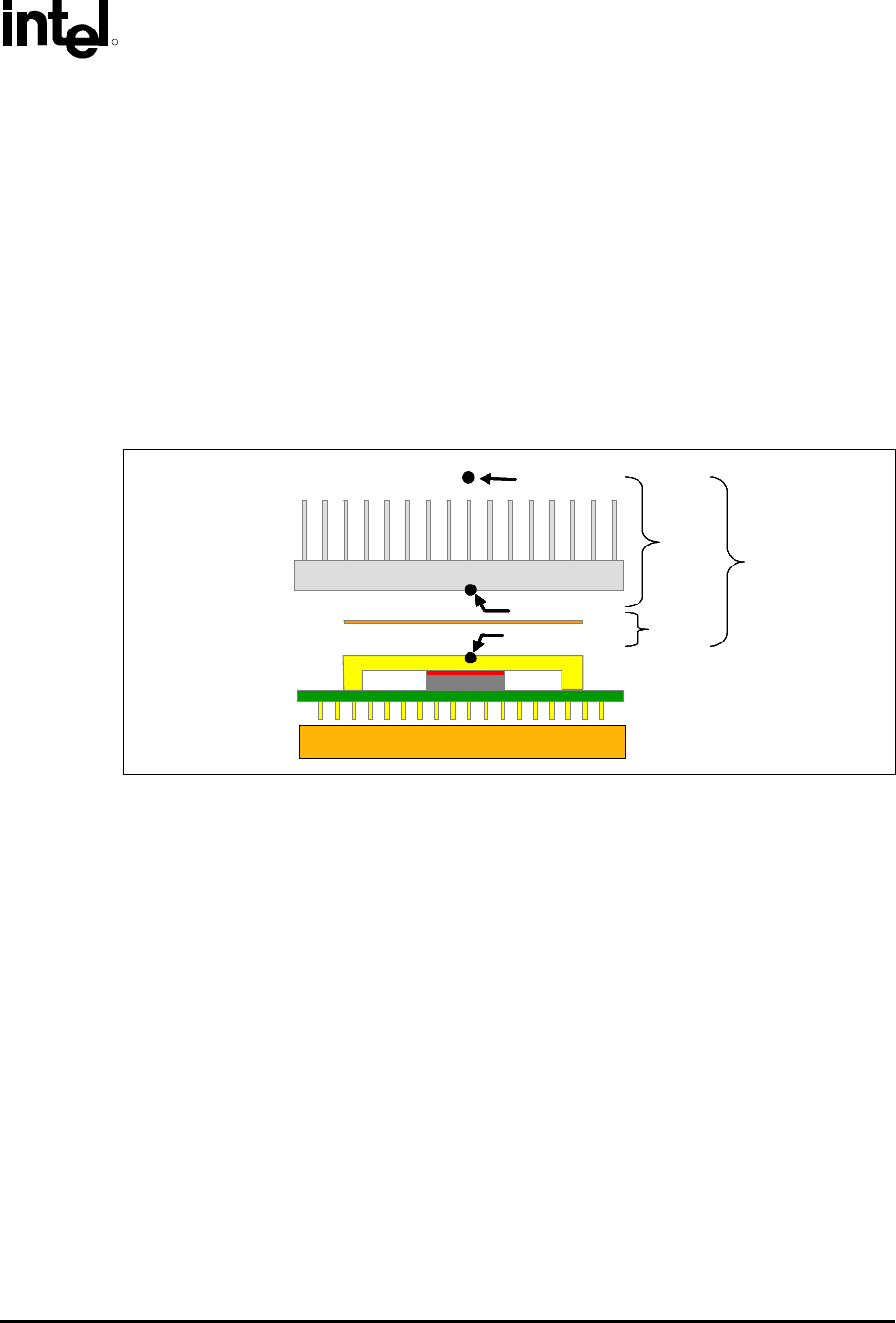
Figure 2-7 illustrates the combination of the different thermal characterization parameters.
Figure 2-7. Processor Thermal Characterization Parameter Relationships
HEATSINK
IHS
TIM
PROCESSOR
T
S
T
C
SOCKET
Ψ
SA
Ψ
CS
Ψ
CA
HEATSINK
IHS
TIM
PROCESSOR
T
S
T
CASE
T
LA
SOCKET
Ψ
SA
Ψ
CS
Ψ
CA
HEATSINK
IHS
TIM
PROCESSOR
T
S
T
C
SOCKET
Ψ
SA
Ψ
CS
Ψ
CA
HEATSINK
IHS
TIM
PROCESSOR
T
S
T
CASE
T
LA
T
LA
SOCKET
Ψ
SA
Ψ
CS
Ψ
CA
Example
The cooling performance, Ψ
CA,
is then defined using the principle of thermal characterization
parameter described above:
• Define a target case temperature T
CASE-MAX
and corresponding TDP at a target frequency, F,
given in the processor datasheet.
• Define a target local ambient temperature at the processor, T
LA
.
Since the processor thermal specifications (T
CASE-MAX
and TDP) can vary with the processor
frequency, it may be important to identify the worse case (lowest Ψ
CA
) for a targeted chassis
(characterized by T
LA
) to establish a design strategy such that a given heatsink can cover a given
range of processor frequencies.
The following provides an illustration of how one might determine the appropriate performance
targets. The example power and temperature numbers used here are not related to any Intel
processor thermal specifications, and are for illustrative purposes only.
Assume the datasheet TDP is 85 W and the case temperature specification is 68 °C for a given
frequency. Assume as well that the system airflow has been designed such that the local processor
ambient temperature is 45°C. The following could be calculated using equation 1 from above for the
given frequency:










