Intel Celeron D Processor 300 Sequence
Table Of Contents
- Contents
- Revision History
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Electrical Specifications
- 2.1 FSB and GTLREF
- 2.2 Power and Ground Lands
- 2.3 Decoupling Guidelines
- 2.4 Voltage Identification
- 2.5 Reserved, Unused, and TESTHI Signals
- 2.6 FSB Signal Groups
- 2.7 GTL+ Asynchronous Signals
- 2.8 Test Access Port (TAP) Connection
- 2.9 FSB Frequency Select Signals (BSEL[2:0])
- 2.10 Absolute Maximum and Minimum Ratings
- 2.11 Processor DC Specifications
- 2.12 VCC Overshoot Specification
- 2.13 GTL+ FSB Specifications
- 3 Package Mechanical Specifications
- 4 Land Listing and Signal Descriptions
- 5 Thermal Specifications and Design Considerations
- 6 Features
- 7 Boxed Processor Specifications
- 8 Debug Tools Specifications
80 Datasheet
Features
6.2.1 Normal State
This is the normal operating state for the processor.
6.2.2 HALT Powerdown State
HALT is a low power state entered when all the logical processors have executed the HALT or
MWAIT instructions. When one of the logical processors executes the HALT instruction, that
logical processor is halted; however, the other processor continues normal operation. The processor
will transition to the Normal state upon the occurrence of SMI#, BINIT#, INIT#, or LINT[1:0]
(NMI, INTR). RESET# will cause the processor to immediately initialize itself.
The return from a System Management Interrupt (SMI) handler can be to either Normal Mode or
the HALT Power Down state. See the Intel Architecture Software Developer's Manual, Volume III:
System Programmer's Guide for more information.
The system can generate a STPCLK# while the processor is in the HALT Power Down state. When
the system de-asserts the STPCLK# interrupt, the processor will return execution to the HALT
state.
While in HALT Power Down state, the processor will process bus snoops.
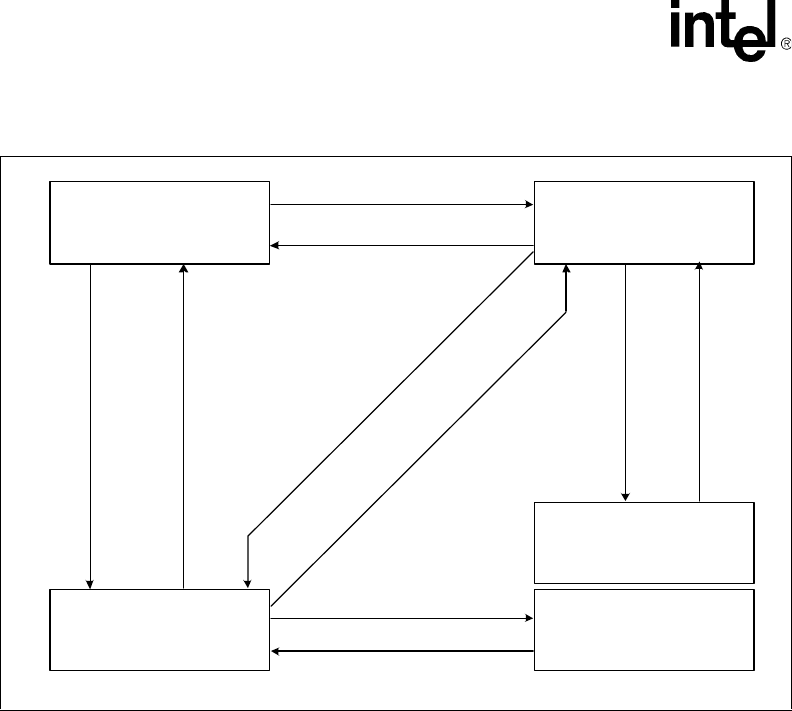
Figure 6-1. Processor Low Power State Machine
HALT State
BCLK running
Snoops and interrupts allow ed
Nor m al State
Normal execution
HALT Snoop State
BCLK running
Service snoops to caches
Stop-Grant State
BCLK running
Snoops and interrupts allow ed
Snoop
Event
Occurs
Snoop
Event
Serviced
INIT#, BINIT#, INTR, NMI, SMI#,
RESET#, FSB interrupts
STPCLK#
Asserted
STPCLK#
De-as serted
S
T
P
C
L
K
#
A
s
s
e
r
t
e
d
S
T
P
C
L
K
#
D
e
-
a
s
s
e
r
t
e
d
Snoop Event Occurs
Snoop Event Serviced
HALT or MWAIT Instruction and
HALT Bus Cycle Generated
Grant Snoop State
BCLK running
Service snoops to caches










