Design Guide
System Memory Design Guidelines (DDR-SDRAM) for SO-DIMM configuration
R
Intel
®
855GM/855GME Chipset Platform Design Guide 111
6.3.7. CPC Signals – SMA[5,4,2,1], SMAB[5,4,2,1]
The GMCH chipset CPC (clock-per-command) signals, SMA[5,4,2,1] and SMAB[5,4,2,1]are “clocked”
into the DDR SDRAM devices using clock signals SCK/SCK#[5:0]. The GMCH drives the CPC and
clock signals together, with the clocks crossing in the valid command window. The GMCH provides
one set of CPC signals per SO-DIMM slot.
Refer to Table 29 for the CKE and CS# signal to SO-DIMM mapping.
Table 36. CPC Signal to SO-DIMM Mapping
Signal Relative To SO-DIMM Pin
SMA[1] SO-DIMM0 AD14
SMA[2] SO-DIMM0 AD13
SMA[4] SO-DIMM0 AD11
SMA[5] SO-DIMM0 AC13
SMAB[1] SO-DIMM1 AD16
SMAB[2] SO-DIMM1 AC12
SMAB[4] SO-DIMM1 AF11
SMAB[5] SO-DIMM1 AD10
The guidelines below should be followed:
• The CPC signal routing should transition from an external layer to an internal signal layer under the
GMCH.
• Keep to the same internal layer until transitioning back out to an external layer to connect to the
appropriate pad of the SO-DIMM connector and the parallel termination resistor.
• If the layout requires additional routing before the termination resistor, return to the same internal
layer and transition back out to an external layer immediately prior to parallel termination resistor.
• External trace lengths should be minimized. Intel suggests that the parallel termination be placed on
both sides of the board to simplify routing and minimize trace lengths.
• All internal and external signals should be ground reference to keep the path of return current
continuous. Intel suggests that all CPC signals be routed on the same internal layer.
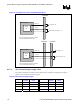
• Resistor packs are acceptable for the parallel (Rt) CPC termination resistors. Figure 50 and Table
37 below depict the recommended topology and layout routing guidelines for the DDR-SDRAM
CPC signals.