Accelerated Graphics Port Interface Specification
AGP3.0 Interface Specification
Rev. 1.0
42
The core-logic or graphics card that supports “universal” AGP3.0 must dynamically change the meaning
of AGPSTAT [2:0] based on the setting of AGPSTAT [3]. The selection of the speed of operation is done
by software, which looks at the supported speeds in the core-logic and graphics card to pick one that is
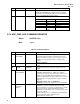
common to both. This speed is programmed into AGPCMD [2:0] as shown in Table 19:
Table 19: Setting Speed of Operation
AGPSTAT[3] AGPCMD[2:0] Speed Selected
0 xxx See AGP2.0 Spec
1 001 4x speed
1 010 8x speed
1 All other codes Reserved
2.4.3 Peer-to-Peer Access
AGP3.0 does not, in general, require the support of PCI Peer-to-Peer accesses. Devices needing to
share data do so through shared buffers in system memory. Note that the AGP3.0 specification
explicitly relaxes some peer-to-peer requirements of the PCI-to-PCI Bridge Specification. Table 20
describes the requirements. In this table, “AGP3.0
a
” represents one AGP3.0 port in the platform. A
“non-AGP3.0
a
” port could be another PCI or some other port. The “type” field represents the transaction
on the initiator’s port.
Table 20: PCI Peer-to-Peer Access
Initiated From Targeted To Type Support
Device(Port == AGP3.0
a
) Device(Port != AGP3.0
a
) AGP3.0 / PCI Read and Write Not Required
Device(Port == AGP3.0
a
) Device(Port == AGP3.0
a
) AGP3.0 / PCI Read and Write Not Required
Device(Port != AGP3.0
a
) Device(Port == AGP3.0
a
) AGP3.0 or PCI Read Not Required
Device(Port != AGP3.0
a
) Device(Port == AGP3.0
a
) AGP3.0 Fast Write or PCI
Write
Required