Intel Pentium 4 Processor CK00 Clock Synthesizer/Driver Design Guidelines
CK00 Clock Synthesizer/Driver Design Guidelines
Page 44
6.3 Spread Spectrum Clocking (SSC) Criteria:
Spread Spectrum functionality on the CK00 class of clock drivers is required and acts as an
on/off switch for different forms of spread spectrum modulation techniques. Any given system
design may or may not use this feature due to platform-level timing issues. The following
specifications are included in the current CK00 definition:
1. No external modulation frequency source is required
2. Vendor needs to synchronously modulate the Host, PCI, 3V66, and CPU/2 output
clocks. REF and fixed frequency 48MHz clock outputs are not modulated.
3. All device timings (including jitter, skew, min-max clock period, output rise/fall time)
MUST meet the existing non-spread spectrum specifications
4. All non-spread Host and PCI functionality must be maintained in the spread
spectrum mode (includes all power management functions.)
5. The minimum clock period cannot be violated. The preferred method is to adjust the
spread technique to not allow for modulation above the nominal frequency. This
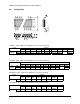
technique is often called “down-spreading”. An example triangular frequency
modulation profile is shown in Figure 5. The modulation profile in a modulation
period can be expressed as:
<<⋅⋅⋅−+
<<⋅⋅⋅+−
=
, )(
; )(
mm
nommnom
m
nommnom
f
1
t
f2
1
when tff2f1
f2
1
t0when tff2f1
f
δδ
δδ
where f
nom
is the nominal frequency in the non-SSC mode, f
m
is the modulation
frequency,
δ
is the modulation amount, and t is time.
(1-
δ
)f
nom
f
nom
1/f
m
t
0.5/f
m
Figure 5 Triangular Frequency Modulation Profile.
6. For triangular modulation, the clock frequency deviation (
δ
) is required to be no more
than 0.6% “down-spread” from the corresponding nominal frequency, i.e., +0%/-
0.6%. The absolute spread amount at the fundamental frequency is shown in Figure
6, as the width of its spectral distribution (between the -3dB roll-off). The ratio of this
width to the fundamental frequency cannot exceed 0.6%. This parameter can be
measured in the frequency domain using a spectrum analyzer. The amount of
allowed spreading for any non-triangular modulation is determined by the induced
downstream PLL tracking skew (see explanation in 8), which cannot exceed that of a
0.6% triangular modulation. Typically, it is about 0.5%.