Intel Pentium 4 Processor CK00 Clock Synthesizer/Driver Design Guidelines
CK00 Clock Synthesizer/Driver Design Guidelines
Page 50
transferred. Indexed bytes are not allowed. However, the Intel controller has a more
specific format than the generic I
2
C protocol.
The clock driver must meet this protocol which is more rigorous than previously stated
I
2
C protocol. Treat the description from the viewpoint of controller. The controller
“writes” to the clock driver and if possible would “read” from the clock driver (the clock
driver is a slave/receiver only and is incapable of this transaction.)
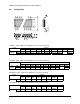
“The block write begins with a slave address and a write condition. After the command
code the host (controller) issues a byte count which describes how many more bytes
will follow in the message. If the host had 20 bytes to send, the first byte would be the
number 20 (14h), followed by the 20 bytes of data. The byte count may not be 0. A
block write command is allowed to transfer a maximum of 32 data bytes.”
1 bit 7 bits 1 1 8 bits 1
Start bit Slave
Address
R/W Ack Command
Code
Ack Byte Count =
N
Ack Data Byte
1
Ack Data Byte
2
Ack ... Data Byte
N
Ack Stop
1 bit 8 bits 1 8 bits 1 8 bits 1 1
Note: The acknowledgment bit is returned by the slave/receiver (the clock driver).
Consider the command code and the byte count bytes required as the first two bytes of
any transfer. The command code is software programmable via the controller, but will
be specified as 0000 0000 in the clock specification. The byte count byte is the number
of additional bytes required for the transfer, not counting the command code and byte
count bytes. Additionally, the byte count byte is required to be a minimum of 1 byte and
a maximum of 32 bytes to satisfy the above requirement.
For example:
Byte count byte Notes:
MSB LSB
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Not allowed. Must have at least one byte.
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 Data for functional and frequency select register (currently byte 0 in
spec)
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 Reads first two bytes of data. (byte 0 then byte 1)
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 Reads first three bytes (byte 0, 1, 2 in order)
0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 Reads first four bytes (byte 0, 1, 2, 3 in order)
0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 Reads first five bytes (byte 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 in order)
0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 Reads first six bytes (byte 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 in order)
0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 Reads first seven bytes (byte 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 in order)
0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 Max byte count supported = 32