Intel Pentium 4 Processor in the 423-pin Package Thermal Solution Functional Specification
Intel® Pentium® 4 Processor Thermal Solution Functional Specification
®
12
base folded fin or high aspect ratio extruded aluminum with high performance attached fans)
has been demonstrated to meet Intel thermal performance requirements.
The use of thermal grease is recommended. Intel’s thermal solution reference designs use
ShinEtsu* G749 thermal grease.
Intel has determined through mechanical characterization that the use of phase change thermal
interface materials may lead to motherboard, processor, and /or surface mount component
damage in mechanical shock or mechanical drop testing. Phase change thermal interface
materials create a strong adhesive bond between the processor package and heat sink that can
lead to large deflections and high loads. The damage induced is not always readily detectable.
The use of phase change thermal interface materials is not recommended. Intel’s thermal
solution reference designs use ShinEtsu* G749 thermal grease.
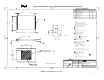
The thermal interface material must be sized and positioned on the heat sink base, covering
Zone B shown in Figure 3, ensuring that the entire processor die area is covered. It will be
important to compensate for heat sink to package attach alignment when selecting the proper
size. If a pre-applied thermal interface material is specified, it may have a protective
application tape, which must be removed prior to attaching the heat sink to the processor.
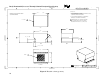
4.8. Heat Sink Clip Requirements
Heat sink attach clips apply force to the heat sink base to maintain desired pressure on the
thermal interface material between the package and the heat sink and help to hold the heat sink
in place under dynamic loading. The Intel reference design heat sink clip will attach to the heat
sink base via the grooves at each end of the base, as shown in Figure 3. The Intel reference
design heat sink clip is latched to the Intel reference design RM clip tabs, one at each end of the
RM.
The heat sink clip reference design is presented in the appendix to this document.
4.9. Retention Mechanism Requirements
Intel has determined through extensive mechanical characterization that the use of direct
chassis attach of the processor retention mechanism can mitigate the risk of mechanical damage
to the motherboard, processor, and other surface mounted components in mechanical shock or
mechanical drop testing. However, direct chassis attach may not mitigate that risk for all
chassis and /or motherboard configurations. Mechanical shock or mechanical drop testing
followed by functional and visual quality checks are required for each chassis-motherboard
configuration.