Mobile Intel Pentium 4 Processor - M and Intel 845MP/MZ Chipset Platform Design Guide
Mobile Intel
®
Pentium
®
4 Processor-M and Intel
®
845MP/845MZ Chipset Platform
62 Design Guide
R
Table 16. Control Signal SO-DIMM Mapping
Signal Relative To SO-DIMM Pin
SCS#[0] SO-DIMM0 121
SCS#[1] SO-DIMM0 122
SCS#[2] SO-DIMM1 121
SCS#[3] SO-DIMM1 122
SCKE[0] SO-DIMM0 96
SCKE[1] SO-DIMM0 95
SCKE[2] SO-DIMM1 96
SCKE[3] SO-DIMM1 95
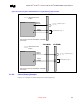
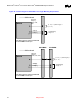
Refer to Figure 24 and Figure 27 for clarification of the description below.
The control signal routing should transition from an external layer to an internal signal layer under the
MCH-M. It should keep to the same internal layer until transitioning back out to an external layer(s) to
connect to the appropriate pad of the SO-DIMM connector and the parallel termination resistor. If the
layout requires return to the same internal layer and transition back out to an external layer immediately
prior to parallel termination resistor.
External trace lengths should be minimized. Intel suggests that the parallel termination be placed on both
sides of the board to simplify routing and minimize trace lengths. All internal and external signals should
be ground referenced to keep the path of the return current continuous. Intel suggests that control be
routed on the same internal layer.
Resistor packs are acceptable for the parallel (Rt) control termination resistors but control signals can’t
be placed within the same Rpacks as data, strobe or command signals. The diagrams and tables below
depict the recommended topology and layout routing guidelines for the DDR-SDRAM control signals
going to SO-DIMM0 or SO-DIMM1.
Figure 24. SO-DIMM0, 1 Control Signal Routing Topology
Vtt
SO-DIMM0,1 PAD
w
MCH-M
Pad
MCH-M Package
Rt
L2
L1