Technical Product Specification
Intel® Server System SC5650HCBRP TPS Power Sub-system
Revision 1.2
Intel order number E81443-002
69
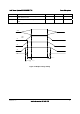
Figure 25. Turn On/Off Timing (Power Supply Signals)
4.1.3.14 Hot Swap Requirement
Hot swapping a power supply is the process of inserting and extracting a power supply from an
operating power system. During this process, the output voltages remain within the capacitive
load limits. Up to two power supplies can be on a single AC line. The power supply hot swaps
by the following method.
Extraction: The AC power disconnects from the power supply as the power supply is
extracted from the system. This can occur in standby mode or power-on mode.
Insertion: The AC power connects to the power supply as the power supply is inserted
into the system. The power supply powers on into either standby mode or power-on
mode.
In general, a failed (off by internal latch or external control) power supply may be removed then
replaced with a good power supply; however, hot swap will work with both operational as well as
failed power supplies. The newly inserted power supply will go into either standby or power-on
mode once inserted.
4.1.3.15 Residual Voltage Immunity in Standby Mode
The power supply is immune to any residual voltage placed on its 12-V output (typically a
leakage voltage through the system from standby output) up to 1000 mV. This residual voltage
does not have any adverse effects on the power supply, including additional power dissipation
or over-stressing / over-heating any internal components or adversely affecting the turn-on
performance (no protection circuits tripping during turn on).
AC Input
Vout
PWOK
5VSB
PSON
T
sb_on_delay
T
AC_on_delay
T
pwok_on
T
vout_holdup
T
pwok_holdup
T
pson_on_delay
T
sb_on_delay
T
pwok_on
T
pwok_off
T
p
T
p
so
n
T
pwok_low
T
sb_vout
AC turn on/off cycle
PSON turn on/off cycle
T
5VSB
_
holdup