Instruction Manual
Table Of Contents
- System bus (CAN) for Lenze PLC devices
- This documentation is valid for ...
- Contents
- 1 Preface and general information
- 2 General information on the system bus (CAN)
- 2.1 Introduction
- 2.2 Interfaces of the Lenze PLCs for system bus connection
- 2.3 Identification of the nodes
- 2.4 Structure of the CAN telegram
- 2.5 Network management (NMT)
- 2.6 Transmission of process data
- 2.7 Transmitting parameter data
- 2.8 Free CAN objects
- 2.9 Application recommendations for the different CAN objects
- 2.10 Monitoring mechanisms
- 3 Configuration (system bus - CAN interface)
- 3.1 CAN baud rate
- 3.2 CAN boot-up
- 3.3 Node address (node ID)
- 3.4 Identifiers of the process data objects
- 3.5 Cycle time (CAN2_OUT/CAN3_OUT)
- 3.6 Delay time (CAN2_OUT/CAN3_OUT)
- 3.7 Synchronisation
- 3.8 Reset node
- 3.9 System bus management
- 3.10 Mapping indexes to codes
- 3.11 Remote parameterisation (gateway function)
- 3.12 Monitoring processes
- 3.13 Diagnostics
- 4 Configuration (AIF interface)
- 5 Configuration (FIF interface)
- 6 Configuration (CAN-AUX system bus interface)
- 7 CAN system blocks
- 8 FIF-CAN system blocks (only Drive PLC)
- 9 CAN-AUX system blocks (only ECSxA)
- 10 LenzeCanDrv.lib function library
- 10.1 Overview
- 10.2 Version identifiers of the function library
- 10.3 L_CanInit - initialising the CAN driver
- 10.4 L_CanClose - deactivating the CAN driver
- 10.5 L_CanGetStatus - querying the driver status
- 10.6 L_CanGetRelocCobId - querying the COB-ID range
- 10.7 L_CanPdoTransmit - transmitting a CAN object
- 10.8 L_CanPdoReceive - receiving a CAN object
- 11 LenzeCanDSxDrv.libfunction library
- 11.1 Overview
- 11.2 Version identifiers of the function library
- 11.3 L_CanDSxInitIndexCode - Configuration of index mapping
- 11.4 L_CanDSxOpen - initialising the CanDSx driver
- 11.5 L_CanDSxClose - deactivating the index mapping
- 11.6 L_CanDSxOpenHeartBeat - initialising a "Heartbeat"
- 11.7 L_CanDSxHeartBeat - carrying out a "Heartbeat"
- 11.8 L_CanDSxCloseHeartBeat - deactivating the "Heartbeat"
- 11.9 L_CanDSxOpenNodeGuarding - initialising the "Node Guarding"
- 11.10 L_CanDSxNodeGuarding - carrying out a "Node guarding"
- 11.11 L_CanDSxCloseNodeGuarding - deactivating the "Node Guarding"
- 12 Index
10.7 L_CanPdoTransmit − transmitting a CAN object
System bus (CAN) for Lenze PLC devices
LenzeCanDrv.lib function library
10−8
L
PLC−Systembus EN 2.0
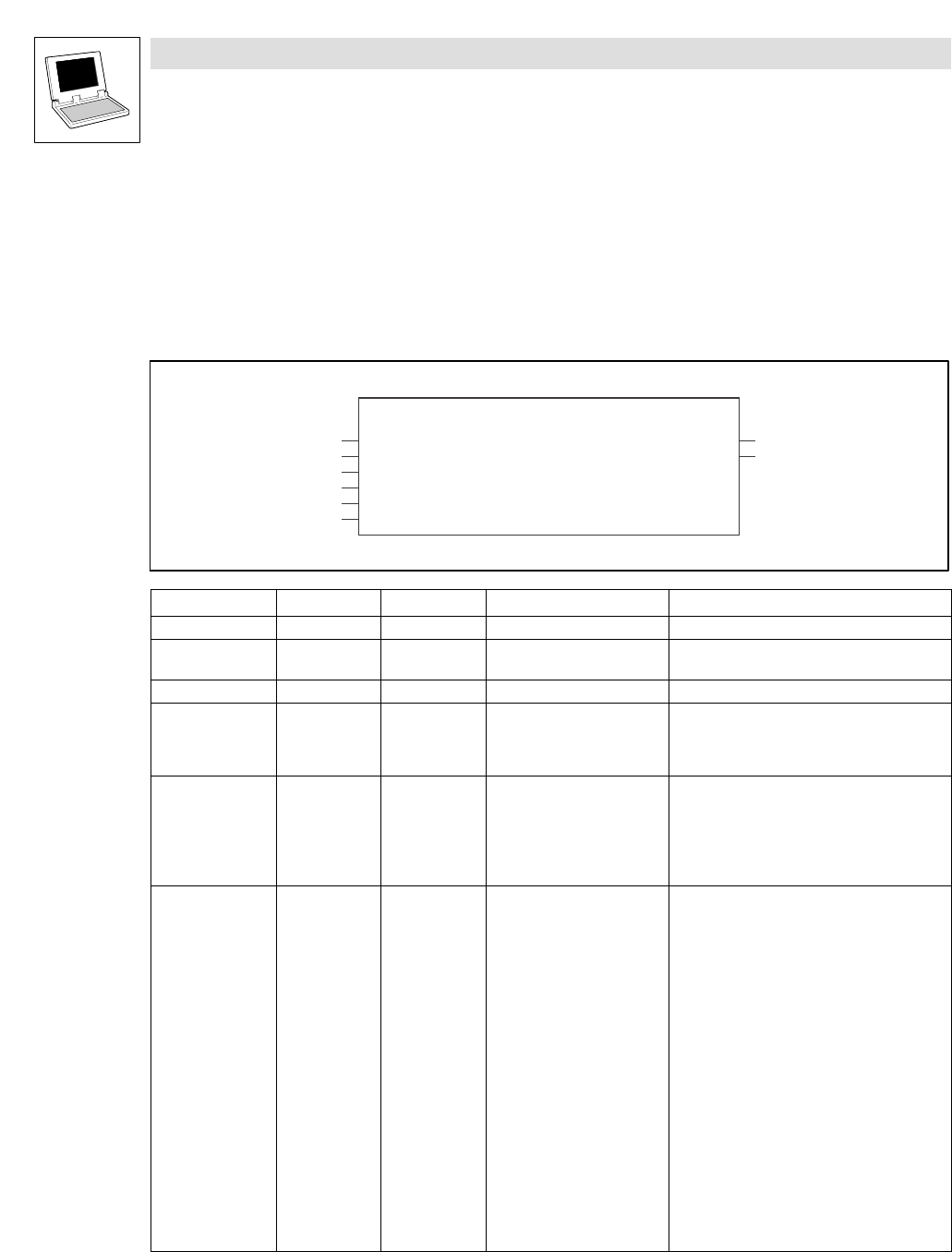
10.7 L_CanPdoTransmit − transmitting a CAN object
Function block
This FB serves to transmit data via the system bus interface according to CANopen.
· The data transmission is carried out simultaneously to the process of the PLC program by the
operating system of the controller, whereby an object can be max. sent every 250 ms.
L_CanPdoTransmit
wDrvNr
byLen
dwCobId
pIOAdress
tRepeatTime
byTransmitMode
nState
wNrOfCallsToSend
Identifier Data type Variable type Possible settings Information
wDrvNr Word VAR_INPUT 10 System bus
byLen Byte VAR_INPUT 0...8 Telegram length (in bytes)
dwCobID Double Word VAR_INPUT 0...2047 CAN identifier
pIOAdress Pointer to Byte VAR_INPUT Pointer to the address in the
memory from which the data
bytes to be transmitted are
stored.
The address of a variable can be determined via
the address function ADR.
tRepeatTime Time VAR_INPUT
T#0s
T#xms
Parameter for the time−controlled transmission
(byTransmitMode = 1/2)
· Transmission takes place at each call of the
FB.
· TRansmission takes place after the set cycle
time x (in ms) has expired.
byTransmitMode Byte VAR_INPUT 0 Event−controlled transmission
· Transmission takes place if the input data
have changed.
· If the bus state changes from
Pre−operational to Operational, the telegram
on principle is transmitted once.
1 Time−controlled transmission
· Transmission takes place after the cycle time
set via
tRepeatTime has expired.
2 Time−controlled transmission with superimposed
event control
· Transmission takes place after the cycle time
set via
tRepeatTime has expired, and if the
transmitted data have changed.
3 Forced transmission
· Transmission takes place if the action
<Instance name>.SendData is
called, irrespective of the cycle time set.










