Printer User Manual
Table Of Contents
- Introduction
- Set Initial Conditions (SIC) Command
- IBM Emulation Mode Printer Commands
- Control Codes
- Escape Sequences
- Printer Command Parameters
- Command Structure
- Printer Command Quick Reference (IBM Emulation Mode)
- Selecting a Character Set
- Select Code Page
- Print From Code Page
- Download a Character Set
- Select Global Font
- Select Print Type Style
- Set Print Quality
- Graphics Print Modes
- Horizontal Movement
- Line Control
- Vertical Tabulation
- Line Spacing
- Set Top of Form and Page Length
- Printer Control
- Epson Emulation Mode Printer Commands
- OKI Microline Emulation Mode Printer Commands
- Using the Printer Interface
- Downloading Characters and Fonts
- Barcodes
- Code Pages
- Glossary
- Index
Section 6: Using the Printer Interface
92
Computer to Printer Communication
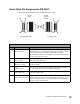
The parallel interface transfers data from computer to printer. The data path is 8
bits wide. The printer and the computer synchronize data transfer with the
interface signals STROBE*, ACKNLG*, and BUSY.
When the computer is ready to send a byte of data to the printer, the computer
puts the byte of data on the data lines. Then the computer sends a STROBE*
(low) pulse to the printer. The printer responds with a BUSY (high) signal.
After the printer receives the data, the printer pulses the ACKNLG* (low) line.
This signals the computer that the printer has read the byte of data into printer
memory. If the printer buffers are not full and the printer can receive more data,
the printer removes the BUSY (low) signal.