Operation Manual
Table Of Contents
- Contents
- Safety information
- About your printer
- Ordering and replacing supplies
- Using the printer control panel buttons and menus
- Using the printer software
- Loading paper and original documents
- Printing
- Tips for printing
- Printing basic documents
- Printing specialty documents
- Working with photos
- Using a memory card or flash drive with the printer
- Supported memory cards and file types
- Printing photos using the printer control panel
- Editing photos using the printer control panel
- Printing photos from a memory device using the printer software
- Printing photos from a PictBridge-enabled digital camera
- Printing photos from a memory device using the proof sheet
- Printing photos from a digital camera using DPOF
- Printing from a Bluetooth-enabled device
- Printing on both sides of the paper (duplexing)
- Managing print jobs
- Copying
- Tips for copying
- Making copies
- Copying photos
- Copying a two-sided document
- Enlarging or reducing images
- Adjusting copy quality
- Making a copy lighter or darker
- Collating copies using the printer control panel
- Repeating an image on one page
- Copying multiple pages on one sheet
- Making a duplex copy
- Canceling copy jobs
- Scanning
- Faxing
- Setting up the printer to fax
- Configuring the fax settings
- Creating a contact list
- Sending faxes
- Receiving faxes
- Faxing FAQ
- If I skipped the fax setup initially, do I need to run the installer again to set up the fax?
- What is a splitter and what type of splitter should I use?
- What is my fax number?
- What is my dialing prefix?
- When do I need to set Auto Answer to On?
- How many rings should I set?
- How do I set the distinctive ring for the printer?
- How can I check the dial tone?
- How do I adjust the speaker volume on the printer?
- How can I make sure that fax calls go to the printer and voice calls go to the answering machine?
- What settings work best with digital voice mail?
- How do I change the resolution of the documents that I fax?
- How do I send a fax at a scheduled time?
- How do I send a fax using a phone calling card?
- How do I know that the fax was sent successfully?
- How do I view the fax history of the printer?
- How do I print a fax on both sides of the paper?
- How do I forward a fax?
- Can I block faxes?
- Can I retrieve failed faxes?
- Networking
- Installing the printer on a wireless network
- Wireless network compatibility
- Supported network security options
- Printing a network setup page
- Information you will need to set up the printer on a wireless network
- Installing the printer on a wireless network
- Installing the printer on other computers
- Interpreting the colors of the Wi-Fi indicator light
- Special wireless installation instructions
- Assigning a static IP address
- Changing wireless settings after installation
- Advanced wireless setup
- Creating an ad hoc wireless network
- Adding a printer to an existing ad hoc wireless network
- Configuring the printer wirelessly using WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup)
- Switching between USB and wireless connections (Windows only)
- Switching between USB and wireless connections (Macintosh only)
- Sharing a printer in a Windows environment
- Sharing a printer in a Macintosh environment
- Networking FAQ
- What is Wi-Fi Protected Setup?
- Where do I find my WEP key or WPA passphrase?
- What is an SSID?
- Where do I find my SSID?
- What is a network?
- How do I find out what type of security my network is using?
- How are home networks configured?
- Why do I need an installation cable?
- How do I attach the installation cable?
- How are infrastructure and ad hoc networks different?
- Finding the signal strength
- How can I improve wireless signal strength?
- How can I make sure my computer and printer are connected to the same wireless network?
- Can I use my printer on a USB and a network connection at the same time?
- What is a MAC address?
- How do I find the MAC address?
- What is an IP address?
- What is TCP/IP?
- How do I locate IP addresses?
- How are IP addresses assigned?
- What is a key index?
- Installing the printer on a wireless network
- Maintaining the printer
- Troubleshooting
- Before you troubleshoot
- Using the Service Center to solve printer problems
- If Troubleshooting does not solve your problem
- Setup troubleshooting
- Jams and misfeeds troubleshooting
- Print troubleshooting
- Copy and scan troubleshooting
- Fax troubleshooting
- Memory card troubleshooting
- Wireless troubleshooting
- Wireless troubleshooting checklist
- Resetting the wireless settings to factory defaults
- Cannot print over wireless network
- The Continue button is unavailable
- Cannot print and there is a firewall on the computer
- Wi-Fi indicator light is not lit
- Wi-Fi indicator light is green but the printer does not print (Windows only)
- Wi-Fi indicator light is still orange
- Wi-Fi indicator light is blinking orange during installation
- Wireless print server not installed
- “Communication not available” message displays when printing wirelessly
- Communication with printer lost when connected to Virtual Private Network (VPN)
- Resolving intermittent wireless communications issues
- Notices
- Product information
- Edition notice
- UNITED STATES GOVERNMENT RIGHTS
- Trademarks
- Licensing notices
- Federal Communications Commission (FCC) compliance information statement
- Hinweis zum GS-Zeichen
- Noise emission levels
- Temperature information
- Waste from Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) directive
- Product disposal
- Battery notice
- ENERGY STAR
- Power consumption
- LEXMARK SOFTWARE LIMITED WARRANTY AND LICENSE AGREEMENTS
- European Community (EC) directives conformity
- Regulatory notices for telecommunication terminal equipment
- Notice to users of the US telephone network: FCC requirements
- South Africa telecommunications notice
- Notice to users of the Canadian telephone network
- Notice to users of the New Zealand telephone network
- Notice to Users in the European Union
- Regulatory notices for wireless products
- Exposure to radio frequency radiation
- Notice to users in Brazil
- Industry Canada (Canada)
- Taiwan NCC RF notice statement
- Notice to users in the European Union
- Index
Routers with security capabilities may allow filtering of MAC addresses on networks. This allows a managed list of
devices to access the network, identified by their MAC addresses. MAC address filtering can help prevent access on
the network from unwanted devices, such as from intruders on a wireless network. MAC address filtering can also
prevent legitimate access if you forget to add a new device to the router's list of allowed addresses. If your network
uses MAC address filtering, be sure to add the MAC address of the printer to the list of allowed devices.
How do I find the MAC address?
Most network equipment has a unique hardware identification number to distinguish it from other devices on the
network. This is called the Media Access Control (MAC) address.
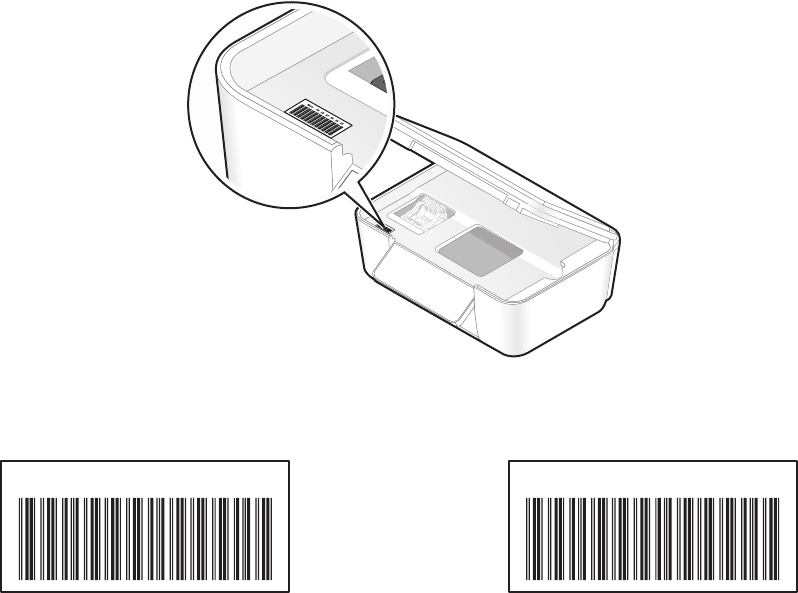
When installing the printer on a network, make sure you select the printer with the correct MAC address.
The MAC address label is located inside the printer.
M
A
C
:
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
The MAC address of the internal print server is a series of letters and numbers. Other devices sometimes use a type of
MAC address called Universally Administered Address (UAA).
MAC: XX XX XX XX XX XX UAA: XX XX XX XX XX XX
Note: A list of MAC addresses can be set on an access point (router) so that only devices with matching MAC addresses
are allowed to operate on the network. This is called MAC filtering. If MAC filtering is enabled in your access point and
you want to add a printer to your network, then the MAC address of the printer must be included in the MAC filter list.
What is an IP address?
An IP address is a unique number used by devices (such as a wireless printer, computer, or wireless access point) on
an IP network to locate and communicate with each other. Devices on an IP network can communicate with each other
only if they have unique and valid IP addresses. A unique IP address means no two devices on the same network have
the same IP address.
An IP address is a group of four numbers separated by periods. An example of an IP address is 192.168.100.110.
Networking
112










