Datasheet
11
LTC2846
sn2846 2846fs
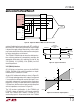
Figure 15. V.28 Driver Propagation Delays
Figure 16. V.28 Receiver Propagation Delays
SWITCHI G TI E WAVEFOR S
UWW
APPLICATIO S I FOR ATIO
WUUU
3V
0V
1.5V
0V
–3V
3V
1.5V
0V
3V
–3V
t
PHL
t
f
V
O
–V
O
D
A
t
PLH
t
r
2846 F15
SR =
6V
t
f
SR =
6V
t
r
V
IH
V
IL
1.5V
1.65V
1.5V
1.65V
t
PHL
V
OH
V
OL
A
R
t
PLH
2846 F16
Overview
The LTC2846 consists of a boost switching regulator, a
charge pump and a 3-driver/3-receiver transceiver. The
boost switching regulator generates a 5V V
CC
from the
3.3V input at V
IN
to power the charge pump and trans-
ceiver. The charge pump generates the V
DD
and V
EE
supplies. The LTC2846’s V
CC,
V
DD
and V
EE
supplies can
be used to power a companion chip like the LTC2844 or
LTC2845. The receiver outputs are driven between 0V and
V
IN
to interface with 3.3V logic.
The LTC2846 and LTC2844 form a complete software-
selectable DTE or DCE interface port that supports the
RS232, RS449, EIA530, EIA530-A, V.35, V.36 and X.21
protocols. Cable termination is provided on-chip, elimi-
nating the need for discrete termination designs.
A complete DCE-to-DTE interface operating in EIA530
mode is shown in Figure 17. The LTC2846 half of each port
is used to generate and appropriately terminate the clock
and data signals. The LTC2844 is used to generate the
control signals along with LL (Local Loopback).
Mode Selection
The interface protocol is selected using the mode select
pins M0, M1 and M2 (see Table 1).
For example, if the port is configured as a V.35 interface,
the mode selection pins should be M2 = 1, M1 = 0, M0 =␣ 0.
For the control signals, the drivers and receivers will
operate in V.28 (RS232) electrical mode. For the clock and
data signals, the drivers and receivers will operate in V.35
electrical mode. The DCE/DTE pin will configure the port
for DCE mode when high, and DTE when low.
The interface protocol may be selected simply by plugging
the appropriate interface cable into the connector. The
mode pins are routed to the connector and are left uncon-
nected (1) or wired to ground (0) in the cable as shown in
Figure 18. The internal pull-up current sources will ensure
a binary 1 when a pin is left unconnected.
The mode selection may also be accomplished by using
jumpers to connect the mode pins to ground or V
IN
.