Datasheet
LTC4313-1/LTC4313-2/
LTC4313-3
10
4313123f
applicaTions inForMaTion
Falling Edge Characteristics
The LTC4313 introduces a propagation delay on falling
edges due to the finite response time and the finite current
sink capability of the buffers. In addition the LTC4313 also
slew limits the falling edge to an edge rate of 45V/µs (typ).
The slew limited falling edge eliminates fast transitions
on the busses and minimizes transmission line effects in
systems. Refer to the Typical Performance Characteristics
section for the propagation delay and fall times as a func-
tion of the bus capacitance.
Stuck Bus Disconnect and Recovery
During an output bus stuck low condition (SCLOUT and
SDAOUT have not been simultaneously high at least once
in 45ms), the LTC4313 attempts to unstick the bus by first
breaking the connection between the input and output. After
40µs the LTC4313 generates up to sixteen 5.5KHz clock
pulses on the SCLOUT pin. Should the stuck bus release
high during this period, clock generation is stopped and
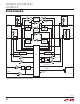
a stop bit is generated. This process is shown in Figure 4
for the case where SDAOUT starts out stuck low and
then recovers. As seen from Figure 4, the LTC4313 pulls
READY low and breaks the connection between the input
and output sides, when a stuck low condition on SDA is
detected. Clock pulses are then issued on SCLOUT to at-
tempt to unstick the SDAOUT bus. When SDAOUT recovers,
clock pulsing is stopped, a stop bit is generated on the
output and READY is released high. When powering up
into a stuck low condition, a connection is never made
between the input and the output, as a stop bit or bus
idle condition is never detected. After a timeout period of
45ms, the behavior is the same as described previously.
Figure 4. Bus Waveforms During SDAOUT
Stuck Low and Recovery Event
4313123 F04
SCLOUT
5V/DIV
READY
5V/DIV
SDAIN
5V/DIV
SDAOUT
5V/DIV
1ms/DIV
DISCONNECT
AT TIMEOUT
STUCK LOW > 45ms
AUTOMATIC CLOCKING
RECOVERS HIGH
DRIVEN LOW
STOP BIT GENERATED