Logic MegaRAID Express User's Guide
Table Of Contents
- 1 Overview
- 2 Introduction to RAID
- 3 RAID Levels
- 4 Features
- 5 Configuring MegaRAID Express 500
- 6 Hardware Installation
- Checklist
- Installation Steps
- Summary
- 7 Cluster Installation and Configuration
- Software Requirements
- Hardware Requirements
- Installation and Configuration
- Driver Installation Instructions under Microsoft Windows 2000 Advanced Server
- Network Requirements
- Shared Disk Requirements
- Cluster Installation
- Installing the Windows 2000 Operating System
- Setting Up Networks
- Configuring the Cluster Node Network Adapter
- Configuring the Public Network Adapter
- Verifying Connectivity and Name Resolution
- Verifying Domain Membership
- Setting Up a Cluster User Account
- Setting Up Shared Disks
- Configuring Shared Disks
- Assigning Drive Letters
- Verifying Disk Access and Functionality
- Cluster Service Software Installation
- Configuring Cluster Disks
- Validating the Cluster Installation
- Configuring the Second Node
- Verify Installation
- SCSI Drive Installations
- Configuring the SCSI Devices
- Terminating the Shared SCSI Bus
- 8 Troubleshooting
- A SCSI Cables and Connectors
- B Audible Warnings
- C Cluster Configuration with a Crossover Cable
- Glossary
- Index
MegaRAID Express 500 Hardware Guide
44
Configuration Strategies,
Continued
Maximizing Drive Availability
You can maximize the availability of data on the physical disk drive in the
logical array by maximizing the level of fault tolerance. The levels of fault tolerance
provided by the RAID levels are:
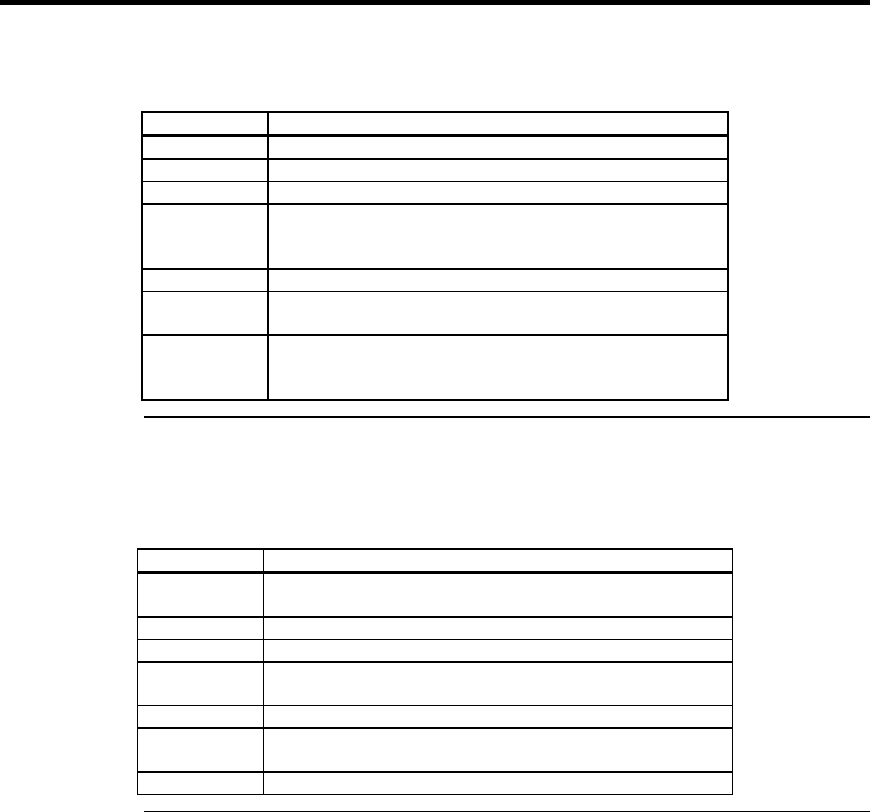
RAID Level Fault Tolerance Protection
0 No fault tolerance.
1 Disk mirroring, which provides 100% data redundancy.
3 100% protection through a dedicated parity drive.
5 100% protection through striping and parity. The data is
striped and parity data is written across a number of physical
disk drives.
10 100% protection through data mirroring.
30 100% protection through data striping. All data is striped
across all drives in two or more arrays.
50 100% protection through data striping and parity. All data is
striped and parity data is written across all drives in two or
more arrays.
Maximizing Drive Performance
You can configure an array for optimal performance. But optimal drive
configuration for one type of application will probably not be optimal for any other
application. A basic guideline of the performance characteristics for RAID drive arrays at
each RAID level is:
RAID Level Performance Characteristics
0 Excellent for all types of I/O activity, but provides no data
security.
1 Provides data redundancy and good performance.
3 Provides data redundancy.
5 Provides data redundancy and good performance in most
environments.
10 Provides data redundancy and excellent performance.
30 Provides data redundancy and good performance in most
environments.
50 Provides data redundancy and very good performance.