Datasheet
2005-2018 Microchip Technology Inc. DS20001826E-page 14
MCP1700
6.0 APPLICATION CIRCUITS AND
ISSUES
6.1 Typical Application
The MCP1700 is most commonly used as a voltage
regulator. Its low quiescent current and low dropout
voltage make it ideal for many battery-powered
applications.
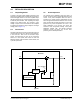
FIGURE 6-1: Typical Application Circuit.
6.1.1 APPLICATION INPUT CONDITIONS
6.2 Power Calculations
6.2.1 POWER DISSIPATION
The internal power dissipation of the MCP1700 is a
function of input voltage, output voltage and output
current. The power dissipation resulting from the
quiescent current draw is so low it is insignificant
(1.6 µA x V
IN
). The following equation can be used to
calculate the internal power dissipation of the LDO.
EQUATION 6-1:
The maximum continuous operating junction
temperature specified for the MCP1700 is +125°C. To
estimate the internal junction temperature of the
MCP1700, the total internal power dissipation is
multiplied by the thermal resistance from junction to
ambient (R
JA
). The thermal resistance from junction to
ambient for the SOT-23 pin package is estimated at
230
°C/W.
EQUATION 6-2:
The maximum power dissipation capability for a
package can be calculated given the junction-to-
ambient thermal resistance and the maximum ambient
temperature for the application. The following equation
can be used to determine the maximum internal power
dissipation of the package.
EQUATION 6-3:
EQUATION 6-4:
Package Type = SOT-23
Input Voltage Range = 2.3V to 3.2V
V
IN
maximum = 3.2V
V
OUT
typical = 1.8V
I
OUT
= 150 mA maximum
GND
V
OUT
V
IN
C
IN
1µF Ceramic
C
OUT
1 µF Ceramic
V
OUT
V
IN
(2.3V to 3.2V)
1.8V
I
OUT
150 mA
MCP1700
P
LDO
V
IN MAX
V
OUT MIN
–I
OUT MAX
=
P
LDO
= Internal power dissipation of the
LDO Pass device
V
IN(MAX)
= Maximum input voltage
V
OUT(MIN)
= Minimum output voltage of the
LDO
T
JMAX
P
TOTAL
R
JA
T
AMAX
+=
T
J(MAX)
= Maximum continuous junction
temperature
P
TOTAL
= Total power dissipation of the device
R
JA
= Thermal resistance from junction to
ambient
T
A(MAX)
= Maximum ambient temperature
P
DMAX
T
JMAX
T
AMAX
–
R
JA
---------------------------------------------------=
P
D(MAX)
= Maximum power dissipation of the
device
T
J(MAX)
= Maximum continuous junction
temperature
T
A(MAX)
= Maximum ambient temperature
R
JA
= Thermal resistance from junction to
ambient
T
JRISE
P
DMAX
R
JA
=
T
J(RISE)
= Rise in the device’s junction
temperature over the ambient
temperature
P
TOTAL
= Maximum power dissipation of the
device
R
JA
= Thermal resistance from junction to
ambient