Data Sheet
SERVOMOTORS
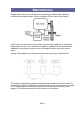
Despite their small size, servomotors are surprisingly complex little machines,
controlled using signal pulses. Here's a diagram of how a servo motor works.
A DC motor (normal motor that can rotate continuously) is attached to a gear box,
which drives the servo arm, but is also coupled to a position sensor that provides
feedback to an electronic control circuit that keeps the servo arm at the correct
angle.
Control of the position uses a series of pulses arriving every 20 milliseconds.
The length of each of these pulses will determine the position of the servo arm. So
a short pulse of just 0.5 milliseconds will put the arm at one end of its travel. A pulse
of 1.5 milliseconds will put the arm at its center position and a maximum pulse
length of 2.5 milliseconds will put it at the other end of its travel.
Page 9