User Guide
II. THE BASICS OF ANALOG SYNTHESIS
For those getting started in the world of electronic music, let’s take a few
moments to go through the basics of sound and synthesis. This will help you
understand what the front panel controls do.
In order to understand synthesis, one must have a basic working knowledge of
the characteristics of sound. There are a few key terms that cover the basics:
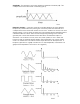
Sound – audible vibrations of air pressure. Electronic sounds are delivered to the air
through loudspeakers. (figure 2)
Frequency– The rate of vibration in sound measured in Hertz (Hz or cycles/second)
(figure 3). Our ears can hear from 20 to 20,000 Hz. Frequency corresponds to the
musical term, pitch. A low frequency corresponds to a low-pitched sound such as
a bass; a high frequency sound corresponds to a high pitched sound such as a
piccolo. In music, a change in pitch of one octave higher equals a doubling of the
frequency.