User Manual
Moxa’s Managed Switch Next Generation OS (v3.x) User Manual
81
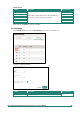
You can view the current MAC Address Table on the bottom part of the configuration page.
Item Name
Description
Index
The number of the MAC address.
VLAN
The VLAN number
MAC Address
The MAC address on this device.
Type
Learnt Unicast, Learnt Multicast, Static Unicast, Static: Multicast
Port
The forwarding port of this MAC address.
QoS
This section describes how QoS works and how to configure the settings.
QoS Overview
The switch’s traffic prioritization capability provides Quality of Service (QoS) to your network by making
data delivery more reliable. You can prioritize traffic on your network to ensure that high priority data is
transmitted with minimum delay. Traffic can be controlled by a set of rules to obtain the required Quality of
Service for your network. The rules define different types of traffic and specify how each type should be
treated as it passes through the switch. The switch can inspect both IEEE 802.1p/1Q layer 2 CoS (Class of
Service) tags, and even layer 3 DSCP (Differentiated Services Code Point) information to provide consistent
classification of the entire network. The switch’s QoS capability improves the performance and determinism
of industrial networks for mission-critical applications.
The Traffic Prioritization Concept
Traffic prioritization allows you to prioritize data so that time-sensitive and system-critical data can be
transferred smoothly and with minimal delay over a network. The benefits of using traffic prioritization are:
• Improve network performance by controlling a wide variety of traffic and by managing congestion.
• Assign priorities to different categories of traffic. For example, set higher priorities for time-critical or
mission-critical applications.
• Provide predictable throughput for multimedia applications, such as video conferencing or voice over IP,
and minimize traffic delay and jitter.
• Optimize the network utilization depending on application usage and usage needs. Hence, asset owners
do not always need to expand their backbone bandwidth as the amount of traffic increases.
Traffic prioritization uses eight traffic queues to ensure that higher priority traffic can be forwarded
separately from lower priority traffic, which guarantees Quality of Service (QoS) to your network.