User`s manual
Table Of Contents
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Getting Started
- 3. Initial IP Address Configuration
- 4. Introducing Serial Port Operation Modes
- 5. Introducing OnCell Central and Ethernet Operation Modes
- 6. Using the Web Console
- 7. Cellular Network Settings
- 8. Configuring Serial Port Operation Modes
- 9. Configuring the Cellular-Enabling Ethernet Device
- 10. Configuring OnCell Central Management Software
- 11. Additional Serial Port Settings
- 12. System Management Settings
- 13. Software Installation/Configuration
- A. Pinouts and Cable Wiring
- B. RFC2217
- C. Dynamic Domain Name Server
- D. Well Known Port Numbers
- E. Auto IP Report Protocol
- F. GSM Alphabet
- G. Default Settings
OnCell G3111/G3151/G3211/G3251 Series User’s Manual Serial Port Operation Modes
4-11
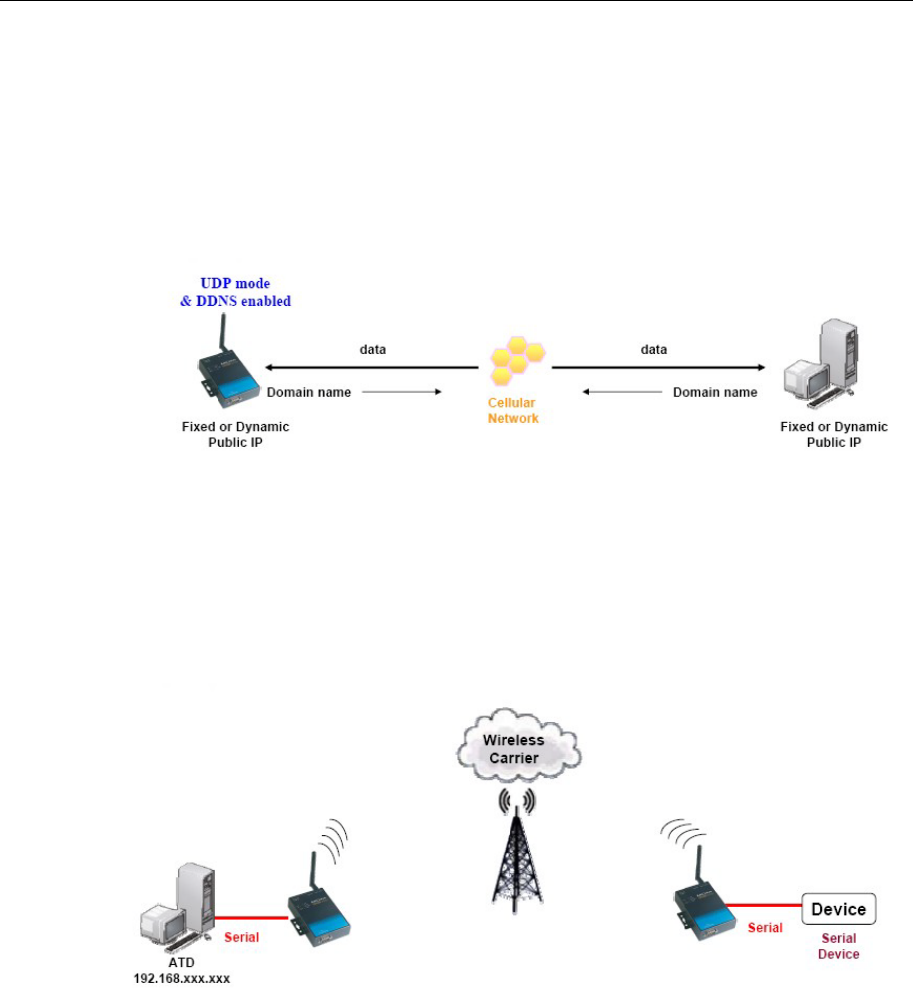
2. Domain name with DDNS.
If your cellular service provider assigns a public IP address after you connect to the cellular
network, you can also access the OnCell G3111/G3151/G3211/G3251 using the domain name.
If your service provider assigns a public IP address (either fixed or dynamic) to your cellular
device and your control center is the side that initiates the connection, you can enable the
DDNS function and UDP mode to allow other devices on the Internet to connect to your
device using its domain name. This will ensure that your device will remain reachable even
when its public IP address is updated. Note that you will need to register your device with a
DDNS server. Please refer to Appendix C for more information.
Ethernet Modem Mode
Ethernet Modem mode is designed for use with legacy operating systems, such as MS-DOS, that
do not support TCP/IP networks. By connecting a properly configured OnCell
G3111/G3151/G3211/G3251 serial port to the MS-DOS computer’s serial port, it is possible to use
legacy software to transmit data over the cellular network, even if the software was originally
designed to transmit data through a modem. In this case, the AT commands are converted into IP
format.










