User`s manual
Table Of Contents
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Getting Started
- 3. Initial IP Address Configuration
- 4. Introducing Serial Port Operation Modes
- 5. Introducing OnCell Central and Ethernet Operation Modes
- 6. Using the Web Console
- 7. Cellular Network Settings
- 8. Configuring Serial Port Operation Modes
- 9. Configuring the Cellular-Enabling Ethernet Device
- 10. Configuring OnCell Central Management Software
- 11. Additional Serial Port Settings
- 12. System Management Settings
- 13. Software Installation/Configuration
- A. Pinouts and Cable Wiring
- B. RFC2217
- C. Dynamic Domain Name Server
- D. Well Known Port Numbers
- E. Auto IP Report Protocol
- F. GSM Alphabet
- G. Default Settings
OnCell G3111/G3151/G3211/G3251 Series User’s Manual Serial Port Operation Modes
5-3
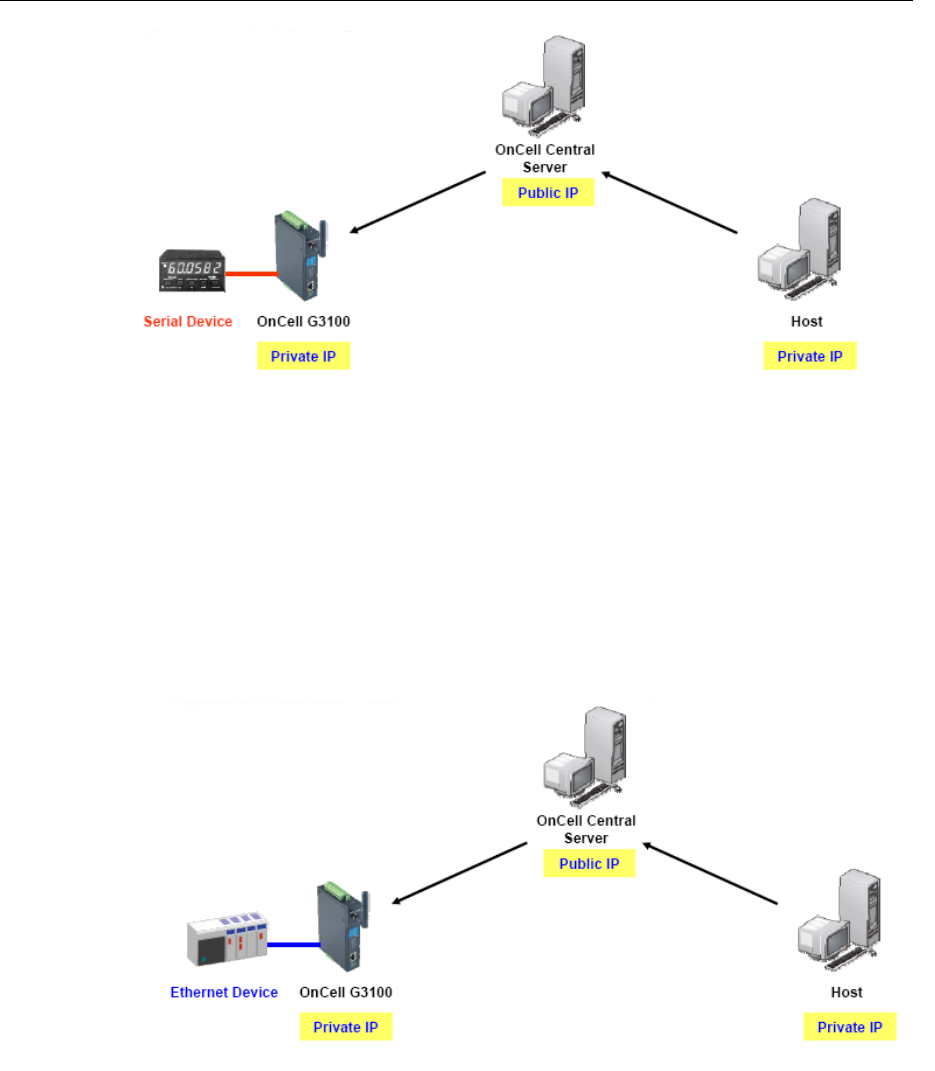
OnCell Central Ethernet Device Connection
If your device uses Ethernet interface, and your cellular service provider assigns you a private IP
address after you connect to the cellular network, service forwarding allows you to access the
OnCell G3100 via an OnCell Central Server from any host PC using either a private IP or public
IP address.
Service forwarding, sometimes referred to as port mapping, is the act of forwarding a network
port from one network node to another. This technique can allow an external user to reach a port
on a private IP address (inside a LAN) from the outside via a NAT-enabled IP gateway (OnCell
G3100’s NAT original is enabled).
Cellular-Enabling Ethernet Device
Note: This function is only supported by the OnCell G3100 Rev.2.0. Please refer to the
Specifications section of Chapter 1 (page 1-3) for more information.
The OnCell G3100 IP gateway works like a router. All Ethernet devices connected to the
OnCell’s LAN port are hidden via the OnCell’s NAT function. This allows any number of local
Ethernet devices to access the Internet using the OnCell as a gateway. However, the OnCell










