Manual
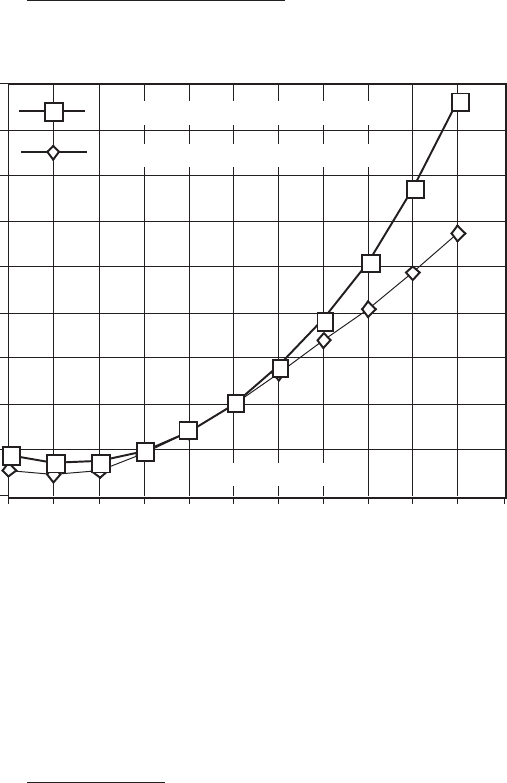
D. A Chart of Comparative Error
Users wanting to measure natural water based solutions to 1% would
have to alter the internal compensation to the more suitable preloaded
based compensation may want to stick with it, regardless of increasing
II will provide the
repeatability and convertibility of data necessary for relative values for
process control.
E. Other Solutions
A salt solution like sea water or liquid fertilizer acts like NaCl. An internal
correction for NaCl can be selected for greatest accuracy with such
sugar solution, or a silicate, or a calcium salt at a high or low temperature
may require a “User” value peculiar to the application to provide readings
close to the true compensated conductivity.
Clearly, the solution characteristics should be chosen to truly represent
the actual water under test for rated accuracy of
±
1%. Many industrial
applications have historically used relative measurements seeking a
7%
Chart 2
55
(1)%
(2)%
0%
1%
2%
3%
4%
5%
6%
0 5 10 15 20
25
30 35 40 45 50
Temperature
NaCl error with KCl tempco
442 error with KCl tempco










