User's Manual
Table Of Contents
- WFS709TP ProSafe Smart Wireless Switch Software Administration Manual
- Contents
- About This Manual
- Chapter 1 Overview of the WFS709TP
- Chapter 2 Deploying a Basic WFS709TP System
- Chapter 3 Configuring Network Parameters
- Chapter 4 RF Plan
- Chapter 5 Configuring WLANS
- Chapter 6 Configuring AAA Servers
- Chapter 7 Configuring 802.1x Authentication
- Chapter 8 Configuring the Captive Portal
- Chapter 9 Configuring MAC-Based Authentication
- Chapter 10 Adding Local WFS709TPs
- Chapter 11 Configuring Redundancy
- Chapter 12 Configuring Wireless Intrusion Protection
- Chapter 13 Configuring Management Utilities
- Chapter 14 Configuring WFS709TP for Voice
- Appendix A Configuring DHCP with Vendor-Specific Options
- Appendix B Windows Client Example Configuration for 802.1x
- Appendix C Internal Captive Portal
- Appendix D Related Documents
- Index
WFS709TP ProSafe Smart Wireless Switch Software Administration Manual
Configuring Wireless Intrusion Protection 12-3
v1.0, June 2007
• Valid AP. An AP that is part of the enterprise providing WLAN service. APs that successfully
connect to the WFS709TP and load software and configuration should be classified as valid
APs.
• Interfering AP or Known Interfering AP. An AP that is seen in the RF environment but is
not connected to the wired network. An interfering AP is not considered a direct security threat
since it is not connected to the wired network.
• Unsecure AP. An rogue AP that is part of the network. A rogue AP is an unauthorized AP that
is plugged into the wired side of the network.
• DoS AP. An AP on which denial of service is enabled.
To manually classify an AP:
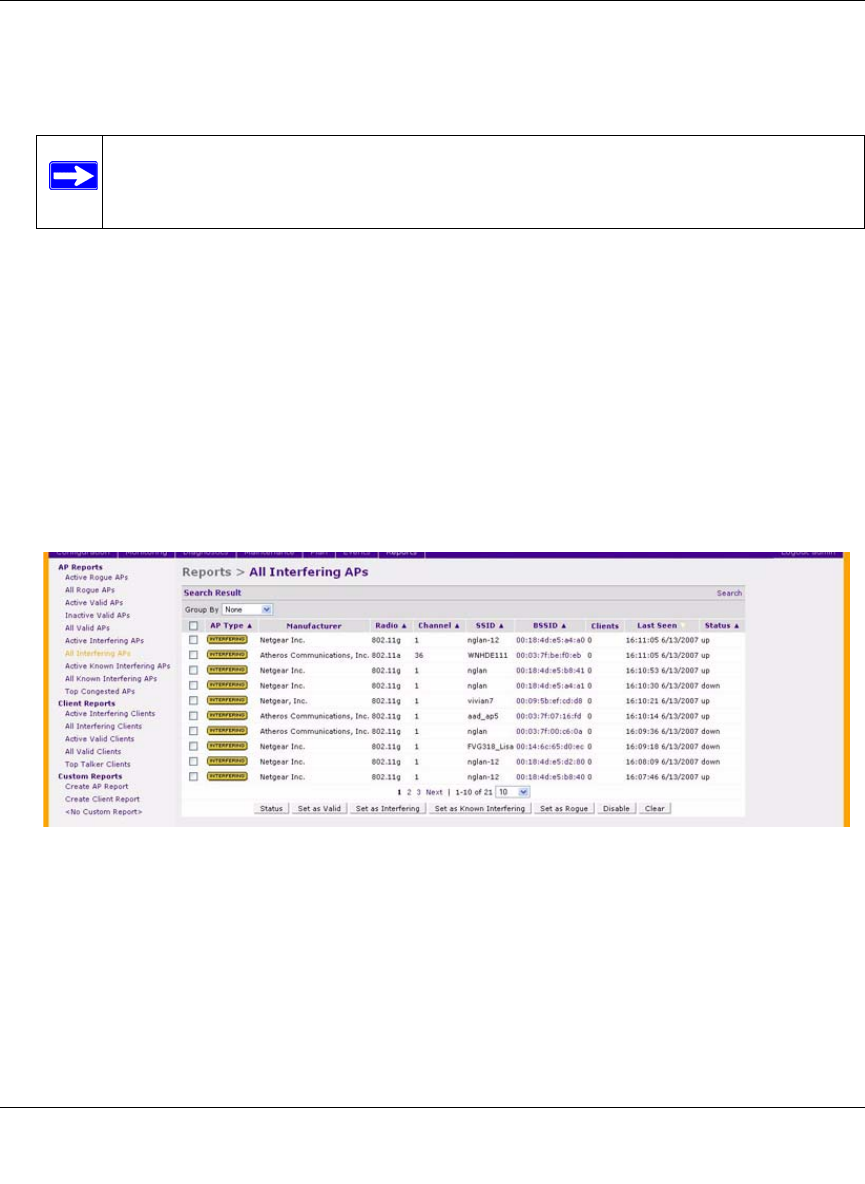
Navigate to the Reports > AP Reports> All Interfering APs page on the master WFS709TP
(Figure 12-2).
4. Select the checkboxes for the APs you want to classify.
5. Click the appropriate “Set as” button on the page.
6. Click Apply.
Note: Any client that successfully authenticates with a valid AP and passes encrypted
traffic is classified as a valid client. (Encrypted traffic includes encrypted
802.11 frames and unencrypted 802.11 frames that are VPN encrypted.)
Figure 12-2










