Computer Hardware User Manual
365
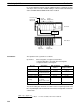
6-2-1 PC with I/O Units Only
Here, we’ll compute the cycle time for a simple PC. The CPU Unit controls only
I/O Units, eight on the CPU Rack and five on a 5-slot Expansion I/O Rack. The
PC configuration for this would be as shown below. It is assumed that the pro-
gram contains 5,000 instructions requiring an average of 0.156 µs each to
execute.
CPU Rack
Expansion I/O Rack
12-point Output Units
8-point Output Unit
16-point Input Units
8-point Input Units 8-point Output Units
Calculations The equation for the cycle time from above is as follows:
Cycle time = Overseeing time + Program execution time + I/O refresh time +
Peripheral device servicing time
Process Calculation With Peripheral
Device
Without
Peripheral Device
Overseeing Fixed 0.7 ms 0.7 ms
Program execution 0.156 µs/instruction
× 5,000 instructions
0.78 ms 0.78 ms
I/O refresh See below. 0.34 ms 0.34 ms
Peripheral device
servicing
Minimum time 0.26 ms 0.0 ms
Cycle time Total of above 2.08 ms 1.82 ms
The I/O refresh time would be as follows for two16-point Input Units, four 8-point
Input Units, two 12-point Output Units (12-point Units are treated as 16-point
Units), and five 8-point Output Units controlled by the PC:
8 pts
(16 pts × 2) + (8 pts × 4)
× 20 µs = 0.34 ms× 20 µs +
8 pts
(16 pts × 2) + (8 pts × 5)
6-2-2 PC with Host Link and Remote I/O Master Units
Here, the cycle time is computed for a PC with a Host Link Unit and Remote I/O
Master Unit installed. The PC configuration for this could be as shown below.
The CPU Unit controls three 8-point Input Units, three 8-point Output Units, a
Host Link Unit, and a Remote I/O Master Unit connected to a Remote I/O Slave
Rack containing four 16-point Input Units and four 12-point Output Units.
Calculating Cycle Time Section 6-2