Specifications
Configuration Tsunami MP.11 5012-SUR Installation and Management
RIP Parameters
72
RIP Parameters
Routing Internet Protocol (RIP) is a dynamic routing protocol you can use to help automatically propagate routing table
information between routers. The unit can be configured as RIPv1, RIPv2, RIPv1 compatible, or a combination of all
three versions while operating in Routing mode. In general, the unit’s RIP module is based upon RFC 1389.
NOTE: RIP does not work when Network Address Translation (NAT) is enabled.
Note the following:
• RIPv2 is enabled by default when routing mode is selected.
• You may turn RIP off by clearing the Enable RIP Interface check box for the Ethernet or the wireless interface. Any
RIP advertisements that are received on the designated interface are ignored. All other options on the page are
dimmed.
• If the Enable RIP Interface check box is selected, the unit sends RIP requests and “listens” for RIP updates coming
from RIP-enabled devices advertising on the network. You may configure the Receive field for RIPv1, RIPv2, or a
combination of both. Although the unit receives and processes these updates, it does not further propagate these
updates unless configured to advertise RIP. Again, you may configure the Advertize field for Do Not Send, RIPv1,
RIPv2, or RIPv1 Compatible.
• The ability to enable or disable default route propagation is not user configurable. Once initialized, the 5012-SUR
uses its static default route and does not advertise this route in RIP updates. If another router on your network is
configured to advertise its default route, this route overwrites the static default route configured on the 5012-SUR.
The 5012-SUR then also propagates the new dynamic default route throughout the network.
Be aware that, once a dynamic default route is learned, it behaves just as any other dynamic route learned through RIP.
This means if the device sending the default route stops sending RIP updates, the default route times out and the unit
has no default route to the network. Workarounds for this condition include rebooting or re-entering a static default route.
In general, the best approach is to disable the propagation of default routes on the other routers in your network unless
you understand the risks.
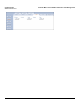
The following table describes the properties and features of each version of RIP supported.
Properties and Features of Supported RIP Versions
RIPv1 RIPv2 RIPv1 Compatible
Broadcast Multicast Broadcast
No Authentication Authentication Authentication
Class routing Classless routing (VLSM) Classless routing (VLSM)
Distance-vector protocol Distance-vector protocol Distance-vector protocol