Owner's manual
DS2705: SHA-1 Authentication Master
6 of 18
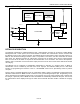
Figure 1. Block Diagram
EEPROM
1-Wire
Master/
Slave
160-bit MAC
Control FSM
64-bit
Challenge
CHAL
PASS
Pullup
Control
VDD
t
CHD
+ t
AAT
VSS
16-bit
Configuration
FAIL
CHP = 0
SDQ
MDQ
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
The DS2705 orchestrates a challenge/response SHA-1 authentication procedure by accessing a Dallas Battery
Management SHA-1 Token product, such as the DS2703 or DS2704. The remote SHA-1 token is accessed with
the MDQ pin acting as the 1-Wire bus master. The DS2705 issues the appropriate 1-Wire command sequence on
MDQ to write the 64-bit challenge, initiates a SHA-1 computation in the token, and then reads back the 160-bit
MAC result. The DS2705 compares the 160-bit MAC received from the battery token with the preprogrammed
MAC. An exact bit for bit match is required for the authentication to be successful. The result of the operation,
PASS or FAIL, is indicated on active low status output pins which can be used to drive status LEDs and/or enable
cell charging.
The DS2705 can be configured to automatically authenticate by detection of a presence pulse on MDQ or
authentication can be controlled by the state of the CHAL input pin. The DS2705’s SDQ pin is a 1-Wire slave
interface for programming the behavior of the I.C.. All EEPROM values can be permanently locked to prevent
corruption.
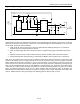
Figure 2 shows a example application circuit for a standalone battery charger. The DS2705 is preprogrammed for
automatic authentication on MDQ and also contains a known good challenge/response pair. Programming occurs
during assembly through PCB test points shown on the right side of the circuit. When a battery pack is inserted into
the charger, a presence pulse on MDQ will cause the DS2705 to automatically authenticate the pack. The result of
the authentication will be displayed through the LEDs and the DS2705 will either enable or disable the charging
circuit.