Owner's manual
DS2705: SHA-1 Authentication Master
9 of 18
AUTHENTICATION SEQUENCE
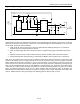
Following the detection of the battery, the DS2705 initiates the authentication sequence. The sequence is executed
in whole each time authentication is initiated. See Figure 4.
1. Test for presence with 1-Wire RESET.
2. Issue SKIP ROM (SKIP NET ADDRESS) command.
3. Issue Write Challenge command with 64-bit Challenge data.
4. Issue Compute MAC without ROMID command to SHA-1 token.
5. Provide strong pullup on DQ output.
6. Issue 8 write 0 timeslots.
7. Issue read time slots to receive MAC from token.
8. Compare local and token MAC results.
9. If configured for multiple attempts, re-try until authentication complete.
10. Test for presence with 1-Wire RESET.
11. Update status on
PASS or FAIL pins.
Note: If the DS2705 does not receive a presence pulse after presence has been established, or the presence
test in step 9. fails, then the status is reported as not present with both the
PASS and FAIL pins hi-Z.
PREPROGRAMMED CHALLENGE AND RESPONSE
A challenge response authentication system does not require a truly random set of challenges. The set of unique
challenges must be sufficiently large that it precludes the use of a lookup table type of attack. If a large enough set
of unique challenges is dispersed over a population of portable devices, then each portable device does not need
to store the secret key and duplicate the computation of the MAC. It need only store one challenge response pair to
provide a practical barrier to battery clones. This system requires that every battery contain the secret key and
SHA-1 algorithm so that it is compatible with any portable device it might be required to power.
The DS2705 stores the preprogrammed challenge and response MAC. This serves to lower the cost and increase
the secrecy of the key since the key does not have to be programmed into the DS2705. Dallas Semiconductor
recommends not using any challenge response pair where either the challenge or MAC is all ‘0’s or all ‘1’s to
prevent accidental authentication of an open or shorted communication bus.