Specifications
The Enhancement of a Multi-Terrain Mechatron for Autonomous Outdoor Applications
52
Shielding
The effect of electromagnetic interference (EMI) from the drive motors was
investigated. A thick aluminium shielding plate was placed between the motors and
driver units to act as a ground plane and direct the noise away from the low power
circuits. The components were also physically separated by the largest distance
possible as noise intensity reduces according to the inverse square of distance.
Neither method produced any noticeable difference to the noise magnitude indicating
it was not radiating through space but rather conducting through the cables. Twisting
the motor cables was also tested to cancel any differential mode noise present
however again this did not completely remedy the underling problem.
Smoothing Capacitors
The fact the noise signal appears at the same frequency as the PWM switching
frequency indicates a problem with the power supply not sourcing sufficient current.
Sealed Lead Acid batteries cannot supply high currents at the required rate because
they are relatively high impedance so as frequency increases the battery resistance
dominates and restricts current flow.
A large variety of high capacity smoothing capacitors were added to the battery
supply rails to act as fast responding charge reservoirs. Low pass filters were also
added to the PWM lines to smooth out the high frequency components of the signal
edges however these methods did not completely remove the noise.
Ferrite Beads
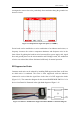
Instead of analyzing the frequency of occurrence of the noise signals (~36 kHz) the
frequency of the actual noise pulse (~20 MHz) was inspected as shown in Figure 3.14.
Ferrite beads can be used to attenuate these high frequency signals and were