Datasheet
Section 5 Interrupt Controller
Rev.7.00 Dec. 24, 2008 Page 112 of 698
REJ09B0074-0700
5.7 Usage Notes
5.7.1 Contention between Interrupt Generation and Disabling
When an interrupt enable bit is cleared to 0 to disable interrupts, the disabling becomes effective
after execution of the instruction.
When an interrupt enable bit is cleared to 0 by an instruction such as BCLR or MOV, if an
interrupt is generated during execution of the instruction, the interrupt concerned will still be
enabled on completion of the instruction, and so interrupt exception handling for that interrupt will
be executed on completion of the instruction. However, if there is an interrupt request of higher
priority than that interrupt, interrupt exception handling will be executed for the higher-priority
interrupt, and the lower-priority interrupt will be ignored.
The same also applies when an interrupt source flag is cleared to 0.
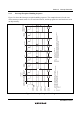
Figure 5.8 shows an example in which the TGIEA bit in the TPU's TIER_0 is cleared to 0.
The above contention will not occur if an enable bit or interrupt source flag is cleared to 0 while
the interrupt is masked.
Internal
address bus
Internal
write signal
φ
TGIEA
TGFA
TGI0A
Interrupt signal
TIER0 write cycle by CPU
TGI0A exception handling
TIER_0 address
Figure 5.8 Contention between Interrupt Generation and Disabling