User Manual Owner's manual
Table Of Contents
- ArmorStart Distributed Motor Controller with EtherNet/IP User Manual
- European Communities (EC) Directive Compliance
- Table of Contents
- Chapter 1
- Product Overview
- Introduction
- Description
- Catalog Number Explanation
- Operation
- Mode of Operation
- Description of Features
- Embedded Switch Technology
- Switched vs. Unswitched Control Power Input/Output (I/O) Connections
- EtherNet/IP™ Ports
- Embedded Web Server
- EtherNet/IP LED Status Indication
- Control Module LED Status and Reset
- Electronic Data Sheet (EDS)
- Fault Diagnostics
- Standard Features
- Factory-Installed Options
- Optional HOA Keypad Configuration (Bulletin 280E/281E only)
- Optional HOA Selector Keypad with Jog Function (Bulletin 284E only)
- Source Brake Contactor and Connector (Bulletin 284E only)
- EMI Filter (Bulletin 284E only)
- Dynamic Brake Connector (Bulletin 284E only)
- IP67 Dynamic Brake Resistor (Bulletin 284E only)
- Output Contactor (Bulletin 284E only)
- Shielded Motor Cable (Bulletin 284E only)
- ArmorStart® EtherNet/ IP Features
- Notes:
- Product Overview
- Chapter 2
- Installation and Wiring
- Receiving
- Unpacking
- Inspecting
- Storing
- General Precautions
- Precautions for Bulletin 280E/281E Applications
- Precautions for Bulletin 284E Applications
- Dimensions
- Mount Orientation
- Operation
- Wiring
- Terminal Designations
- Control Power Wiring
- ArmorStart with EtherNet/IP Internal Wiring
- AC Supply Considerations for Bulletin 284E Units
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC)
- Grounding
- ArmorConnect Power Media
- ArmorConnect Connections
- ArmorConnect Cable Ratings
- Ethernet and I/O Connections
- Power Connections
- Optional Locking Clip
- Installation and Wiring
- Chapter 3
- Chapter 4
- Chapter 5
- Chapter 6
- Chapter 7
- Bulletin 280E/281E/284E Programmable Parameters
- Basic Setup Parameters
- Parameter Groups
- ArmorStart EtherNet/IP Parameters
- Bulletin 280E/281E
- Bulletin 284E
- Basic Status Group
- Produced Assembly Config Group
- Starter Protection Group
- User I/O Configuration Group
- Miscellaneous Configuration Group
- Drive I/O Configuration Group (Bulletin 284E only)
- Drive Display Group (Bulletin 284E only)
- Drive Setup Group (Bulletin 284E only)
- Drive Advanced Setup Group (Bulletin 284E only)
- Clear a Type 1 Fault and Restart the Drive
- Clear an Overvoltage, Undervoltage, or Heatsink OvrTmp Fault without Restarting the Drive
- How StepLogic Works
- StepLogic Settings
- Linear List of Parameters for Bulletin 280E/281E and Bulletin 284E
- Bulletin 280E/281E/284E Programmable Parameters
- Chapter 8
- Chapter 9
- Chapter 10
- Chapter 11
- Chapter 12
- Appendix A
- Applying More Than One ArmorStart Motor Controller in a Single Branch Circuit on Industrial Machinery
- Introduction
- ArmorStart LT Product Family
- Multiple-Motor Branch Circuits and Motor Controllers Listed for Group Installation – General
- Maximum Fuse Ampere Rating According to 7.2.10.4(1) and 7.2.10.4(2)
- Explanatory Example
- Input and Output Conductors of Bulletin 290E and 291E Controllers (a)
- Input and Output Conductors of Bulletin 294E Controllers (b)
- Combined Load Conductors (c)
- Applying More Than One ArmorStart Motor Controller in a Single Branch Circuit on Industrial Machinery
- Appendix B
- CIP Information
- High Level Product Description
- CIP Explicit Connection Behavior
- CIP Object Requirements
- Identity Object
- Assembly Object
- Connection Manager Object
- Discrete Input Point Object
- Discrete Output Point Object
- Parameter Object
- Parameter Group Object
- Discrete Input Group Object
- Discrete Output Group Object
- Control Supervisor Object
- Overload Object
- Device Level Ring (DLR) Object
- Qos Object
- DPI Fault Object
- DPI Alarm Object
- Interface Object
- TCP/IP Interface Object
- Ethernet Link Object
- CIP Information
- Appendix C
- Using DeviceLogix
- DeviceLogix Programming
- DeviceLogix Programming Example
- Import and Export
- Bulletin 284 - VFD Preset Speed Example
- DeviceLogix Ladder Editor Example
- ArmorStart 280 and 281 Status Bits
- Bulletin 280 and 281 ArmorStart Fault Bits
- Bulletin 280 and 281 ArmorStart Outputs
- Bulletin 280 and 281 ArmorStart Produced Network Bits
- Bulletin 284 ArmorStart Status Bits
- Bulletin 284 ArmorStart Fault Bits
- Bulletin 284 ArmorStart Outputs
- Bulletin 284 ArmorStart Produced Network Bits
- Using DeviceLogix
- Appendix D
- Appendix E
- Appendix F
- Back Cover

Rockwell Automation Publication 280E-UM001B-EN-P - July 2012 47
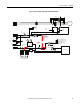
Installation and Wiring Chapter 2
• Using an EMI filter, with any drive rating, may result in relatively high
ground leakage currents. Therefore, the filter must only be used in
installations that are solidly grounded (bonded) to the building power
distribution ground. Grounding must not rely on flexible cables and
should not include any form of plug or socket that would permit
inadvertent disconnection. Some local codes may require redundant
ground connections. The integrity of all connections should be
periodically checked.
Wiring
Wire in an industrial control application can be divided into three groups: power,
control, and signal. The following recommendations for physical separation
between these groups is provided to reduce the coupling effect:
• Minimum spacing between different wire groups in the same tray should
be 6 in. (16 cm).
• Wire runs outside an enclosure should be run in conduit or have shielding/
armor with equivalent attenuation.
• Different wire groups should be run in separate conduits.
• Minimum spacing between conduits containing different wire groups
should be 3 in. (8 cm).
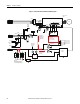
Grounding
An effectively grounded product is one that is “intentionally connected to earth
through a ground connection or connections of sufficiently low impedance and
having sufficient current-carrying capacity to prevent the buildup of voltages
which may result in undue hazard to connected equipment or to persons” (as
defined by the US National Electric Code NFPA70, Article 100B). Grounding
is done for two basic reasons: safety (defined above) and noise containment or
reduction. While the safety ground scheme and the noise current return circuit
may sometimes share the same path and components, they should be considered
different circuits with different requirements.
Grounding Safety Grounds
The object of safety grounding is to ensure that all metalwork is at the same
ground (or Earth) potential at power frequencies. Impedance between the drive
and the building scheme ground must conform to the requirements of national
and local industrial safety regulations or electrical codes. These will vary based
on country, type of distribution system and other factors. Periodically check the
integrity of all ground connections.