Manual
Introduction to Programming
Chapter 10
1
0
-
1
7
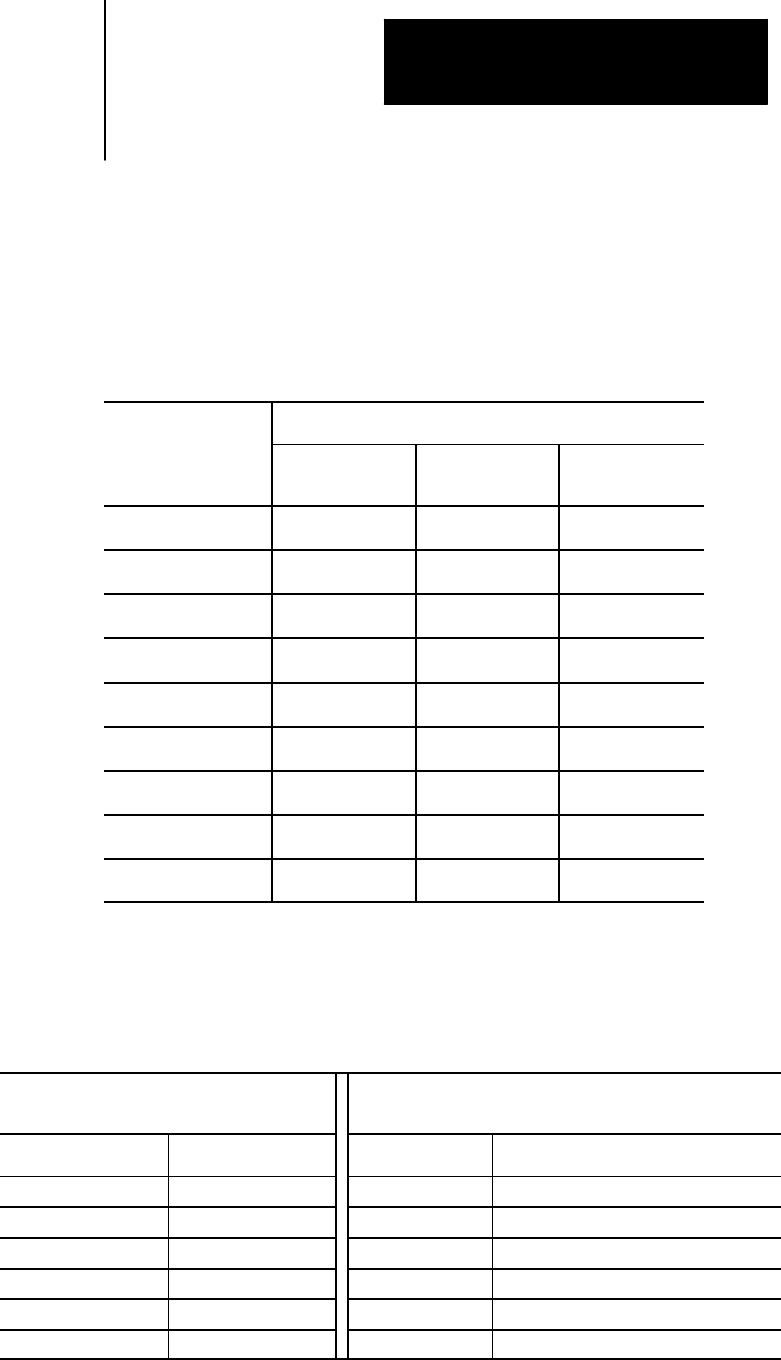
Table 10.A shows the effects of leading zero suppression (LZS) and
trailing zero suppression (TZS). It presumes that your system installer has
set a format of X5.2 (integer 5 digits, decimal 2 digits) in AMP. Different
formats would result in different decimal point placement compared to
those shown below, but the end result would be comparable.
Table 10.A
How the Control Interprets Numeric Values
Position Interpretedby the Control
Programmed X Value TZS Disabled
LZS Disabled
TZS Disabled
LZS Enabled
TZS Enabled
LZS Disabled
X123456. ERROR ERROR ERROR
X12345.6 12345.60 12345.60 12345.60
X1234.56 1234.56 1234.56 1234.56
X123.456 123.45 123.45 123.45
X12345 12345.00 123.45 12345.00
X012345 ERROR 123.45 1234.50
X123456 ERROR 1234.56 12345.60
X1234567 ERROR 12345.67 12345.67
X12345678 ERROR ERROR ERROR
Using LZS and TZS with G-Codes
The following table illustrates how the control interprets different G-Codes
in leading zero and trailing zero suppression modes.
Leading ZeroSuppression Mode
(decimal assumed atend if notprogrammed)
Trailing Zero SuppressionMode
(2-digitG-codeassumedunlessdecimal pointprogrammed)
Program this: Results in this: Program this: Results in this:
G02 2 G02 2
G2 2 G2 20
G2. 2 G2. 2
G92 92 G92 92
G920 920 G920 920 or 92 (if no AMPdefined macro920)
G92.1 92.1 G92.1 92.1










