Manual

Introduction to Programming
Chapter 10
1
0
-
2
3
Important: G-codes can also be expressed in terms of a parametric
expression (for example G[#12+6]). For details, see chapter 28.
Example 10.8 explains execution of modal G-codes, using G00 and G01,
both classified into the same G-code group.
Example 10.8
Programming Modal G-codes
G00 X1. Z2.; G00 modeis effective
Z3. ;
G00 mode is effective
G01 X2. Z1. ;
G01 mode is madeeffective
X3. Z3. ;
G01 mode is ineffect
G00 X1.Z2. ;
G00 mode becomes effective again
G01 G00 Z3, ;
G00 mode is ineffect
G01 G91 Z2 ;
G01 and G91 both ineffect
Example 10.9 is an example of non-modal G-code execution.
Example 10.9
Programming Non-modal G-codes
G00 X1. Z21 ; G00 modeis effective
G28 X2.;
G28 mode, this block only
X2. Z1. ;
G00 mode is effective
G04 P2. X4. ;
G04 active followed by move inG00
Example 10.10
Changing Modes Mid-block
N10G90X10G91Y10;
X10 is absolute (G90) Y10 isincremental (G91).
N20X20;
X20 is incremental (G91).
N30X30G90Y10;
X30 is incremental (G91), Y10is absolute(G90).
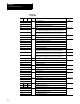
Table 10.E breaks down the G-codes into their modal groups. For
example, G-codes in group 01 are modal only with other G-codes in group
01. G-codes in the 00 group are non-modal, and they are effective only in
the block in which they are programmed.
The 9/Series control provides 3 G-code systems. They are systems A, B,
and C. Your system installer determines which G-code system is used for
a specific application in AMP.
Important: This manual makes the assumption that G-code system C is
used.