User Manual
Multi-Function Gigabit Wireless-N Client Bridge
Version 1.0
25
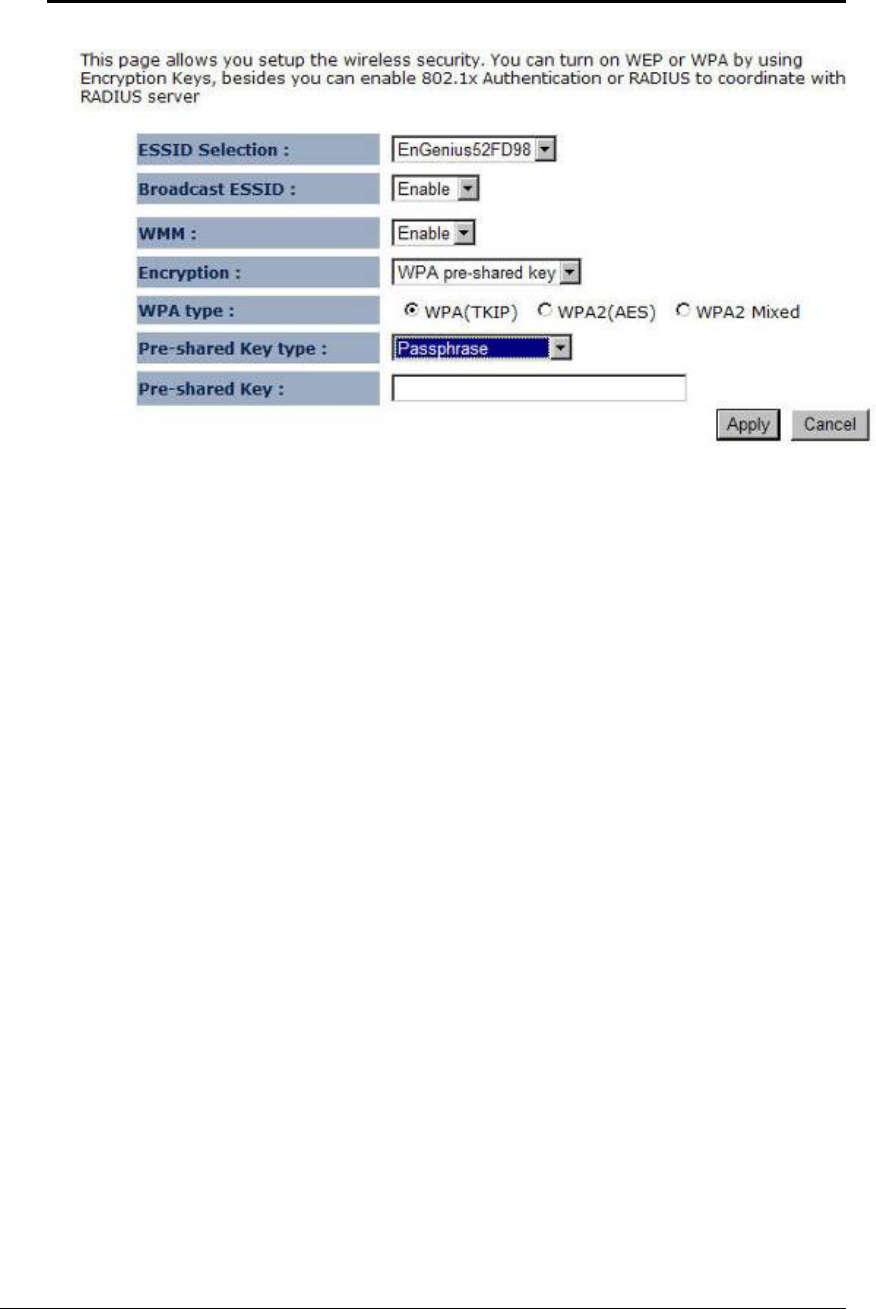
ESSID Selection: As this device supports multiple SSIDs, it is possible to configure a
different security mode for each SSID (profile). Select an SSID from the drop-down list.
Broadcast SSID: Select Enable or Disable from the drop-down list. This is the SSID
broadcast feature.
When this option is set to Enable, your wireless network name is broadcast to
anyone within the range of your signal
. If you're not using encryption then they could connect to
your network. When this is disabled, you must enter the Wireless Network Name (SSID) on
the client manually to connect to the network.
WMM: Choose to Enable or Disable WMM. This is the Quality of Service (QoS) feature for
prioritizing voice and video applications. This option can be further configured in WMM
under the Wireless drop-down menu.
Encryption: Select WPA pre-shared key from the drop-down list.
WPA Type: Select TKIP, AES, or WPA2 Mixed. The encryption algorithm used to secure
the data communication. TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol) provides per-packet key
generation and is based on WEP. AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) is a very secure
block based encryption. Note that, if the bridge uses the AES option, the bridge can associate
with the access point only if the access point is also set to use only AES.
Pre-shared Key Type:: The Key Type can be passphrase or Hex format.
Pre-Shared Key: The key is entered as a pass-phrase of up to 63 alphanumeric characters in
ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange) format at both ends of the
wireless connection. It cannot be shorter than eight characters, although for proper security it
needs to be of ample length and should not be a commonly known phrase. This phrase is used
to generate session keys that are unique for each wireless client.
Click on the Apply button to save the changes.
3.2.4.2.4.4 WPA RADIUS (802.1x)
Click on the Security link under the Wireless drop-down menu.
WPA encryption. WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) was designed to improve upon the security
features of WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy). The technology is designed to work with
existing Wi-Fi products that have been enabled with WEP. WPA provides improved data
encryption through the Temporal Integrity Protocol (TKIP), which scrambles the keys using a
hashing algorithm and by adding an integrity checking feature which makes sure that keys
haven’t been tampered with.










