User Manual
Multi-Function Gigabit Wireless-N Client Bridge
Version 1.0
8
g) Wired LAN backup
Network managers implement wireless LANs to provide backup for mission-critical
applications running on wired networks.
h) Training/Educational facilities
Training sites at corporations and students at universities use wireless connectivity to
ease access to information, information exchanges, and learning.
1.6 Network Configuration
To better understand how the wireless LAN products work together to create a wireless
network, it might be helpful to depict a few of the possible wireless LAN PC card network
configurations. The wireless LAN products can be configured as:
a) Ad-hoc (or peer-to-peer) for departmental or SOHO LANs.
b) Infrastructure for enterprise LANs.
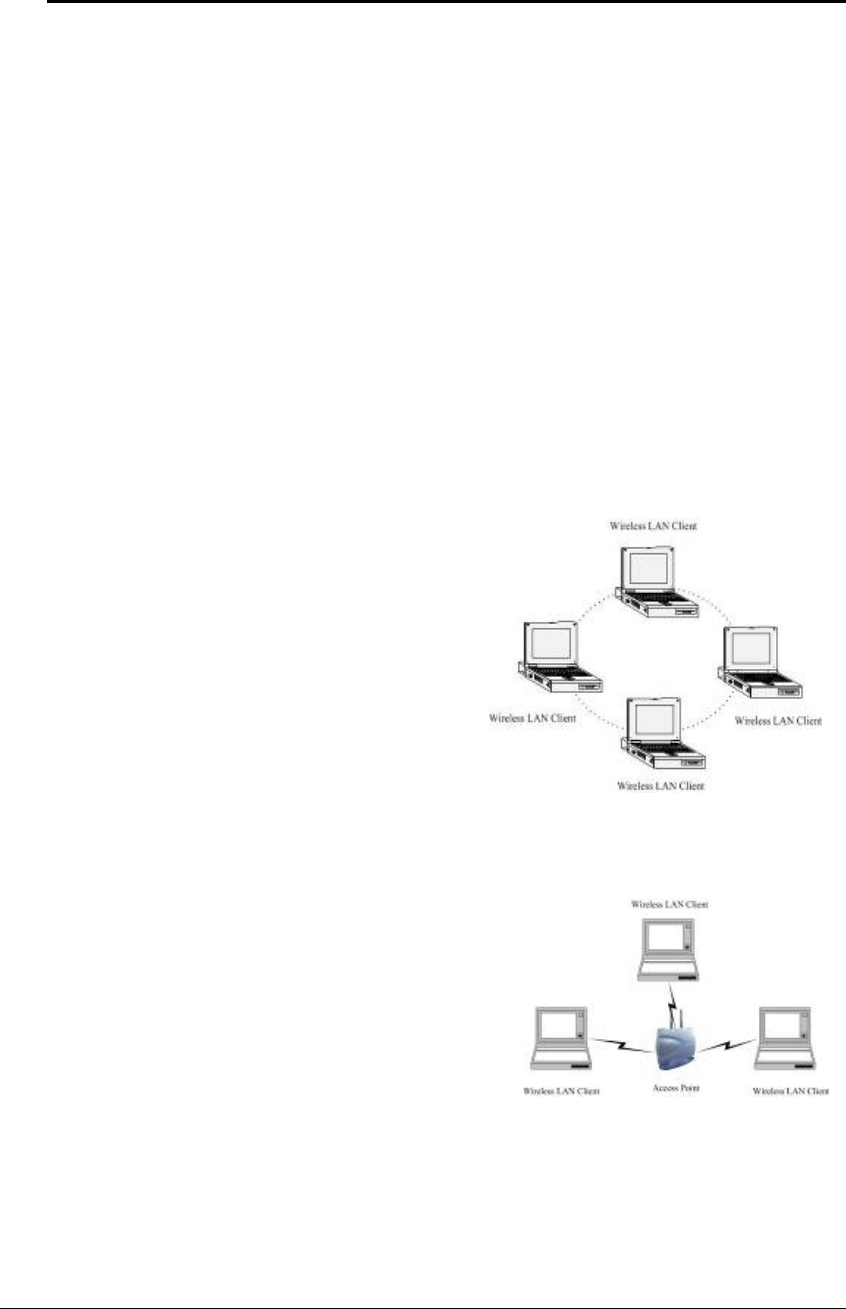
a) Ad-hoc (peer-to-peer) Mode
This is the simplest network
configuration with several
computers equipped with the PC
Cards that form a wireless network
whenever they are within range of
one another. In ad-hoc mode, each
client is peer-to-peer, would only
have access to the resources of the
other client and does not require an
access point. This is the easiest and
least expensive way for the SOHO
to set up a wireless network. The
image depicts a network in ad-hoc
mode.
b) Infrastructure Mode
The infrastructure mode requires the use
of an access point (AP). In this mode,
all wireless communication between
two computers has to be via the AP. It
doesn’t matter if the AP is stand-alone
or wired to an Ethernet network. If used
in stand-alone, the AP can extend the
range of independent wireless LANs by
acting as a repeater, which effectively
doubles the distance between wireless stations. The image below depicts a
network in infrastructure mode.










