User`s manual
Table Of Contents
- Safety Precautions
- Table of contents
- Chapter 1: Outline
- 1-1 Features
- 1-2 Controller
- 1-3 Measurement program
- [1] Positional deviation measurement
- [2] Degree of match inspection
- [3] Lead inspection
- [4] BGA/CSP inspection (IV-S32M/S33M)
- [5] Area measurement by binary conversion
- [6] Object counting by binary conversion
- [7] Object identification by binary conversion
- [8] Point measurements
- [9] Distance and angle measurement
- [10] Multiple position measurement (IV-S33M)
- [11] Multiple degree of match inspection (IV-S33M)
- Chapter 2 : Precautions for Use
- Chapter 3 : System Configuration
- Chapter 4 : Part Names and Functions
- Chapter 5 : Connection and Installation Methods
- Chapter 6 : Setting and Operating Outlines
- Chapter 7 : Simplified Menu Operation
- 7-1 Operation screen
- 7-2 Image display
- 7-3 Setting functions that are different with each controller
- 7-4 Setting procedures
- 7-5 Setting the operation conditions
- 7-6 Setting object types
- 7-7 Setting the shutter speed
- 7-8 Setting the positioning conditions
- 7-9 Setting the existence inspection conditions
- 7-10 Measurement triggering
- 7-11 Saving data
- 7-12 Specify the system conditions
- Chapter 8 : Specifications
- Chapter 9 : Operation Examples
- Glossary
- Appendix
- Alphabetical Index
1-10
Outline
1
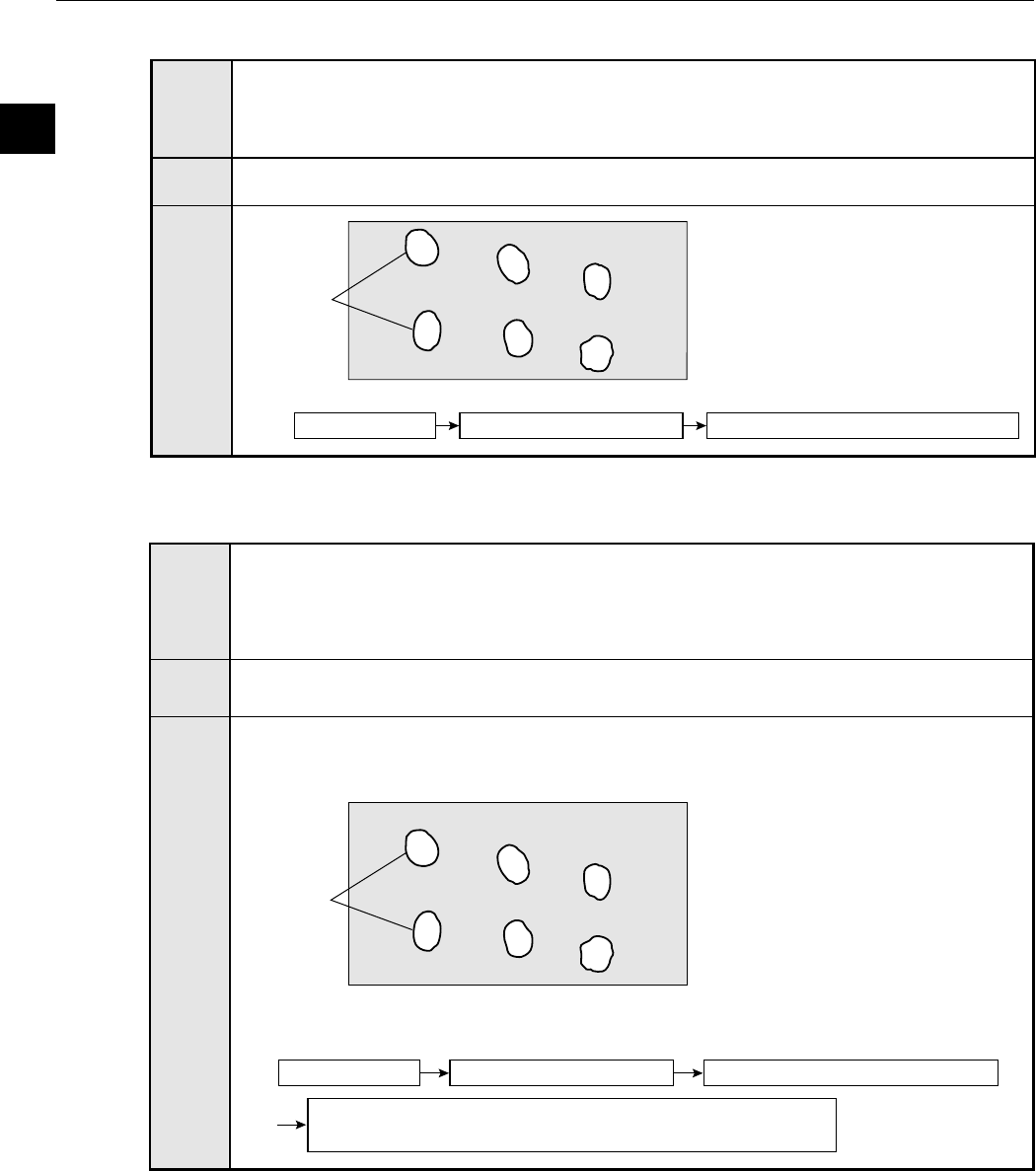
[7] Object identification (labeling) by binary conversion
Objects
No.1 No.2
No.3
No.5No.4
No.6
When there are several objects and the measuring position is arbitrary, the presence or
absence of objects and the size of the objects can be determined.
- The specified pixel area is converted to a binary image. The number of objects, total size
of the white area (the objects) and the area, center of gravity, main axis angle, fillet
diameter, center point, and circumference of each white area can be measured.
- Inspection procedure
Pur-
pose
Exam-
ple
Appli-
cation
Counting the number of food products or parts, measuring the sloped angle or center of
gravity of parts, and measuring the size of food products.
[Measurement of 6 objects]
Measurement (area, gravity center, main axis angle,
fillet diameter, circumference, and center point)
Image capture Convert to binary values
[Measured result]
- Object identification (numbering),
number of objects present, total
area.
- Center point (IV-S33M only),area,
center of gravity, main axis angle,
fillet diameter, circumference, and
center point of each object.
Object identification (numbering)
[6] Object counting by binary conversion
- Inspection procedure
Capture image
Convert to binary values Measure (quantity, total area size)
Workpiece
Pur-
pose
Exam-
ple
Appli-
cation
Checks the number of objects (max. 3000 pcs.) when there is more than one object in an
image arranged arbitrary.
- When the specified pixel field has been converted to a binary image, the white areas
are measured or identified as separate objects and counted.
Counting pieces of food or parts
[Measured result]
- Number of workpieces/total area
size










