User's Manual
Table Of Contents
47
III Features & Configurations | Tenda
4 Advanced Applications
This section includes the following:
To remotely access the device via a domain name or access a server on a
LAN PC, see 4.1 DDNS Settings.
To let an Internet user access your LAN PC without any restriction, see
4.2 DMZ Host.
To automatically map the ports between WAN and LAN, see 4.3 UPNP.
To enable the remote W eb management feature, see 4.4 Remote Web
Management.
To regulate bandwidth, see 4.5 Bandwidth Control (Available only in
4G600).
To restrict your LAN PCs to access certain services on the Internet via
their IP addresses, see 4.6 Client Filter (Available only in 4G600) .
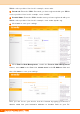
4.1 DDNS Settings
Dynamic DNS or DDNS is a term used for the updating in real time of Internet
Domain Name System (DNS) name servers. We use a numeric IP address
allocated by Internet Service Provider (ISP) to connect to the Internet; the
address may either be stable ("static"), or may change from one session on the
Internet to the next ("dynamic"). However, a numeric address is inconvenient to
remember; an address which changes unpredictably makes connection
impossible. The DDNS provider allocates a static hos t name to the user;
whenever the user is allocated a new IP address this is communicated to the
DDNS provider by software running on a computer or network device at that
address; the provider distributes the association between the host name and
the address to the Internet's DNS servers so that they may resolve DNS queries.
Thus, uninterrupted access to devices and services whose numeric IP address
may change is maintained.
Click Advanced -> DDNS Settings to enter the screen below.