User Manual
27
AUTOMATIC CONTROL
1 HEATING CONTROL BT Reason for energy savings
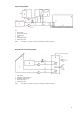
1.1 Emission control 1
The control system is installed at the emitter or
room level, for case 1 one system can control
several rooms.
0 No automatic control of the room temperature The highest supply output is continuously
delivered to the heat emitters resulting in the
supply of unnecessary thermal energy under
part load conditions.
1 Central automatic control
There is only central automatic control acting
either on the distribution or on the generation.
This can be achieved for example by an outside
temperature controller conforming to EN 12098-1
or EN 12098-3; one system can control several
rooms.
Supply output depending on the outside
temperature for example (corresponding to the
probable heat demand of the consumers).
Energy losses under part load conditions are
reduced, but no advantage can be taken of
individual heat gains in the rooms.
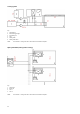
2 Individual room control
By thermostatic valves or electronic controller
2
Supply output based on room temperature
(= controlled variable). It considers heat
sources in the room as well (heat from solar
radition, people, animals, technical equipment).
The room can be kept comfortable with less
energy.
Comment:
Electronic control equipments ensures higher
energy efficiency than thermostatic valves
(higher control accuracy, coordinated
manipulated variable acts on all valves in the
room).
3
Individual room control
By thermostatic valves or electronic controller
3
Same reason as above. In addition:
Central ...
· schedulers make it possible to reduce
output during non-occupancy,
· operating and monitoring functions
further optimize plant operation.
3
Individual room control with communication
As above, in addition:
For integrated plants the heat emission e.g. floor
heating, wall heating, etc. the function 1.1.3 is
assigned to the BA class A.
3
Same reason as above. With this a similar
energy efficient operation can bie achieved for
integrated plants for heat emission as with
function 1.1.4
4
Individual room control with communication and
occupancy detection:
Between controllers and BACS; Demand control /
occupancy detection (this function level is usually
not applied to any slow reacting heat emission
systems with relevant thermal mass, e.g. floor
heating, wall heating).
4
Same reason as above. In addition:
· Effective occupancy control results in
additional energy savings in the room
under part load conditions.
· Demand-controlled energy provision
(production of energy) results in
minimum losses in provision and
distribution.