Basic Documentation
Table Of Contents
Laboratories
Direct Pressure Control
The direct pressure control method uses a room pressure controller with a static pressure
sensing arrangement. This enables the controller to modulate the room’s supply and total
exhaust airflows as needed to maintain the room static pressure set point.
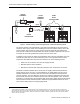
Figure 5 shows the essential components of a typical chemical laboratory room ventilation
system using a single duct supply terminal. The room ventilation system may be either CAV
or VAV with the room airflow being precisely controlled by the Fume Hood Controllers and
the Room Controller.
The Fume Hood Controllers modulate the exhaust airflow of the Fume Hoods to always
maintain the proper amount of exhaust. For constant air volume (CAV) fume hoods, the fume
hood exhaust is maintained at a constant value regardless of the amount that the fume hood
sash is open. For variable air volume (VAV) fume hoods, the fume hood exhaust is
modulated so that the fume hood face velocity (incoming airflow) is maintained at the desired
constant value.
The specific amount of air exhausted by a VAV fume hood depends on the extent that the
sash is open
8
. Aside from controlling the fume hood exhaust airflow, each Fume Hood
Controller also provides an output signal to the Room Controller that represents the amount
of fume hood exhaust airflow. This output signal keeps the Room Controller apprised of the
amount of exhaust air that is being exhausted by each fume hood in the room.
In addition to the air that is being exhausted from the fume hoods, air may also be exhausted
from the laboratory room by the Room General Exhaust that is directly controlled by the
Room Controller. A Room General Exhaust is often required for VAV laboratories with VAV
fume hoods to allow more air to enter the room from the supply terminal to maintain sufficient
room ventilation or maintain the desired room temperature when the fume hood sashes are
closed.
The Room Controller also maintains direct control over the Supply Terminal that provides the
supply make-up air for the room. In a CAV laboratory, the supply airflow into the room is
normally maintained at a constant value since the fume hood exhaust normally remains
constant. However, in a VAV laboratory, the room exhaust depends on the fume hood
exhaust, which varies in accordance with the fume hood sash position. Thus, the Room
Controller in a VAV laboratory must modulate both the incoming supply airflow via the Supply
Terminal and the Room General Exhaust to maintain a proper balance between the total
room exhaust airflow and the incoming supply airflow.
In a VAV laboratory, the Room Controller must modulate the Room General Exhaust to
ensure that there is sufficient total room exhaust to meet the required minimum room
ventilation rate (ACH) rate. The Room Controller must also modulate the Room General
Exhaust to ensure that there is sufficient total room exhaust for the amount of supply airflow
necessary to maintain the room’s ambient temperature.
8
A VAV fume hood controller uses an airflow sensor and a modulating damper in the fume hood exhaust to maintain the
required exhaust airflow in accordance with the fume hood’s total open sash area. This ensures that fume hood face velocity
remains constant for all sash positions. Each VAV fume hood controller continuously sends the fume hood exhaust airflow
value to the room controller.
Siemens Building Technologies, Inc. 21