Technical data
Table Of Contents
- Title
- Preface
- Contents
- 1 Organization Blocks
- 1.1 Overview of the Organization Blocks (OBs)
- 1.2 Program Cycle Organization Block (OB1)
- 1.3 Time-of-Day Interrupt Organization Blocks ( OB10 to OB17)
- 1.4 Time-Delay Interrupt Organization Blocks ( OB20 to OB23)
- 1.5 Cyclic Interrupt Organization Blocks (OB30 to OB38)
- 1.6 Hardware Interrupt Organization Blocks ( OB40 to OB47)
- 1.7 Status Interrupt OB (OB 55)
- 1.8 Update Interrupt OB (OB 56)
- 1.9 Manufacturer Specific Interrupt OB (OB57)
- 1.10 Multicomputing Interrupt Organization Block (OB60)
- 1.11 Synchronous Cycle Interrupt OBs (OB 61 to OB 64)
- 1.12 Technology Synchronization Interrupt OB (OB 65)
- 1.13 I/O Redundancy Error OB (OB70)
- 1.14 CPU Redundancy Error OB (OB72)
- 1.15 Communication Redundancy Error OB (OB73)
- 1.16 Time Error Organization Block (OB80)
- 1.17 Power Supply Error Organization Block (OB81)
- 1.18 Diagnostic Interrupt Organization Block (OB82)
- 1.19 Insert / Remove Module Interrupt Organization Block ( OB83)
- 1.20 CPU Hardware Fault Organization Block (OB84)
- 1.21 Priority Class Error Organization Block (OB85)
- 1.22 Rack Failure Organization Block (OB86)
- 1.23 Communication Error Organization Block (OB87)
- 1.24 Processing Interrupt OB (OB 88)
- 1.25 Background Organization Block (OB90)
- 1.26 Startup Organization Blocks (OB100, OB101 and OB102)
- 1.27 Programming Error Organization Block (OB121)
- 1.28 I/O Access Error Organization Block (OB122)
- 2 Common Parameters for SFCs
- 3 Copy and Block Functions
- 3.1 Copying Memory Area with SFC 20 "BLKMOV"
- 3.2 Uninterruptible Copying of Variables with SFC 81 " UBLKMOV"
- 3.3 Initializing a Memory Area with SFC 21 "FILL"
- 3.4 Creating a Data Block with SFC 22 "CREAT_DB"
- 3.5 Deleting a Data Block with SFC 23 "DEL_DB"
- 3.6 Testing a Data Block with SFC 24 "TEST_DB"
- 3.7 Compressing the User Memory with SFC 25 " COMPRESS"
- 3.8 Transferring a Substitute Value to Accumulator 1 with SFC 44 " REPL_ VAL"
- 3.9 Generating Data Blocks in Load Memory with SFC 82 " CREA_ DBL"
- 3.10 Reading from a Data Block In Load Memory with SFC 83 " READ_ DBL"
- 3.11 Writing a Data Block in Load Memory with SFC 84 " WRIT_ DBL"
- 3.12 Creating a Data Block with SFC 85 "CREA_DB"
- 4 SFCs for Controlling Program Execution
- 5 SFCs for Handling the System Clock
- 6 SFCs for Handling Run-Time Meters
- 7 SFCs/SFBs for Transferring Data Records
- 7.1 Writing and Reading Data Records
- 7.2 Reading Defined Parameters with SFC 54 " RD_ DPARM"
- 7.3 Reading Predefined Parameters with SFC 102 " RD_ DPARA"
- 7.4 Writing Dynamic Parameters with SFC 55 "WR_PARM"
- 7.5 Writing Default Parameters with SFC 56 "WR_DPARM"
- 7.6 Assigning Parameters to a Module with SFC 57 " PARM_ MOD"
- 7.7 Writing a Data Record with SFC 58 "WR_REC"
- 7.8 Reading a Data Record with SFC 59 "RD_REC"
- 7.9 Further Error Information for SFCs 55 to 59
- 7.10 Reading Predefined Parameters with SFB 81 " RD_ DPAR"
- 8 DPV1 SFBs According to PNO AK 1131
- 9 SFCs for Handling Time-of-Day Interrupts
- 9.1 Handling Time-of-Day Interrupts
- 9.2 Characteristics of SFCs 28 to 31
- 9.3 Setting a Time-of-Day Interrupt with SFC 28 " SET_ TINT"
- 9.4 Canceling a Time-of-Day Interrupt with SFC 29 " CAN_ TINT"
- 9.5 Activating a Time-of-Day Interrupt with SFC 30 " ACT_ TINT"
- 9.6 Querying a Time-of-Day Interrupt with SFC 31 " QRY_ TINT"
- 10 SFCs for Handling Time-Delay Interrupts
- 11 SFCs for Handling Synchronous Errors
- 12 SFCs for Handling Interrupts and Asynchronous Errors
- 12.1 Delaying and Disabling Interrupt and Asynchronous Errors
- 12.2 Disabling the Processing of New Interrupts and Asynchronous Errors with SFC 39 " DIS_ IRT"
- 12.3 Enabling the Processing of New Interrupts and Asynchronous Errors with SFC 40 " EN_ IRT"
- 12.4 Delaying the Processing of Higher Priority Interrupts and Asynchronous Errors with SFC 41 " DIS_ AIRT"
- 12.5 Enabling the Processing of Higher Priority Interrupts and Asynchronous Errors with SFC 42 " EN_ AIRT"
- 13 SFCs for Diagnostics
- 13.1 System Diagnostics
- 13.2 Reading OB Start Information with SFC 6 "RD_SINFO"
- 13.3 Reading a System Status List or Partial List with SFC 51 " RDSYSST"
- 13.4 Writing a User-Defined Diagnostic Event to the Diagnostic Buffer with SFC 52 " WR_ USMSG"
- 13.5 Determining the OB Program Runtime with SFC 78 " OB_ RT"
- 13.6 Diagnosis of the Current Connection Status with SFC 87 " C_ DIAG"
- 13.7 Identifying the Bus Topology of a DP Master System with SFC 103 " DP_ TOPOL"
- 14 SFCs and SFBs for Updating the Process Image and Processing Bit Fields
- 14.1 Updating the Process Image Input Table with SFC 26 " UPDAT_ PI"
- 14.2 Updating the Process Image Output Table with SFC 27 " UPDAT_ PO"
- 14.3 Updating the Process Image Partition Input Table in a Synchronous Cycle with SFC 126 " SYNC_ PI"
- 14.4 Updating the Process Image Partition in a Synchronous Cycle with SFC 127 " SYNC_PO"
- 14.5 Setting a Bit Field in the I/O Area with SFC 79 "SET"
- 14.6 Resetting a Bit Field in the I/O Area with SFC 80 " RSET"
- 14.7 Implementing a Sequencer with SFB 32 "DRUM"
- 15 System Functions for Addressing Modules
- 15.1 Querying the Logical Base Address of a Module with SFC 5 " GADR_ LGC"
- 15.2 Querying the Module Slot Belonging to a Logical Address with SFC 49 " LGC_ GADR"
- 15.3 Querying all Logical Addresses of a Module with
- 15.4 Determining the Slot Belonging to a Logical Address with SFC 71 " LOG_ GEO"
- 15.5 Determining the Slot Belonging to a Logical Address
- 16 SFCs for Distributed I/Os or PROFINET IO
- 16.1 Triggering a Hardware Interrupt on the DP Master with SFC 7 " DP_ PRAL"
- 16.2 Synchronizing Groups of DP Slaves with SFC 11 " DPSYC_ FR"
- 16.3 Deactivating and Activating DP Slaves/PROFINET IO Devices with SFC 12 " D_ ACT_ DP"
- 16.4 Reading Diagnostic Data of a DP Slave with SFC 13 " DPNRM_ DG" ( Slave Diagnostics)
- 16.5 Reading Consistent Data of a DP Standard Slave// PROFINET IO Device with SFC 14 " DPRD_DAT"
- 16.6 Writing Consistent Data to a DP Standard Slave/ PROFINET IO Device with SFC 15 " DPWR_DAT"
- 17 PROFInet
- 17.1 Background Information on SFCs 112, 113 and 114
- 17.2 Updating the Inputs of the User Program Interface for the PROFInet Component with SFC 112 " PN_ IN"
- 17.3 Updating the Outputs of the PROFInet Interface for the PROFInet Component with SFC 113 " PN_ OUT"
- 17.4 Updating DP Interconnections with SFC 114 "PN_DP"
- 18 FBs for Cyclical Access to User Data according to the PNO
- 18.1 Introduction to the FBs for Cyclical Access to User Data according to the PNO
- 18.2 Read All Inputs of a DP Standard Slave/PROFINET IO Device with FB 20 " GETIO"
- 18.3 Write All Outputs of a DP Standard Slave/PROFINET IO Device with FB 21 " SETIO"
- 18.4 Read a Part of the Inputs of a DP Standard Slave/ PROFINET IO Device with FB 22 " GETIO_PART"
- 18.5 Write a Part of the Outputs of a DP Standard Slave/ PROFINET IO Device with FB 23 " SETIO_PART"
- System Software for S7- 300/ 400 System and Standard Functions Volume 1/ 2
- Contents
- 19 SFCs for Global Data Communication
- 20 Overview over the S7 Communication and the S7 Basic Communication
- 21 S7 Communication
- 21.1 Common Parameters of the SFBs/FBs and SFCs/FCs for S7 Communication
- 21.2 Startup Routine of SFBs for Configured S7 Connections
- 21.3 How SFBs React to Problems
- 21.4 Uncoordinated Sending of Data with SFB 8/FB 8 " USEND"
- 21.5 Uncoordinated Receiving of Data with SFB/FB 9 " URCV"
- 21.6 Sending Segmented Data with SFB/FB 12 "BSEND"
- 21.7 Receiving Segmented Data with SFB/FB 13 "BRCV"
- 21.8 Writing Data to a Remote CPU with SFB/FB 15 "PUT"
- 21.9 Read Data from a Remote CPU with SFB/FB 14 "GET"
- 21.10 Sending Data to a Printer with SFB 16 "PRINT"
- 21.11 Initiating a Warm or Cold Restart on a Remote Device with SFB 19 " START"
- 21.12 Changing a Remote Device to the STOP State with SFB 20 " STOP"
- 21.13 Initiating a Hot Restart on a Remote Device with SFB 21 " RESUME"
- 21.14 Querying the Status of a Remote Partner with SFB 22 " STATUS"
- 21.15 Receiving the Status Change of a Remote Device with SFB 23 " USTATUS"
- 21.16 Querying the Status of the Connection Belonging to an SFB Instance with SFC 62 " CONTROL"
- 21.17 Querying the Connection Status with FC 62 " C_ CNTRL"
- 21.18 Work Memory Requirements of the S7 Communication SFBs/ FBs
- 22 Communication SFCs for Non-Configured S7 Connections
- 22.1 Common Parameters of the Communication SFCs
- 22.2 Error Information of the Communication SFCs for Non- Configured S7 Connections
- 22.3 Sending Data to a Communication Partner outside the Local S7 Station with SFC 65 " X_ SEND"
- 22.4 Receiving Data from a Communication Partner outside the Local S7 Station with SFC 66 " X_ RCV"
- 22.5 Writing Data to a Communication Partner outside the Local S7 Station with SFC 68 " X_ PUT"
- 22.6 Reading Data from a Communication Partner outside the Local S7 Station with SFC 67 " X_ GET"
- 22.7 Aborting an Existing Connection to a Communication Partner outside the Local S7 Station with SFC 69 " X_ ABORT"
- 22.8 Writing Data to a Communication Partner within the Local S7 Station with SFC 73 "I_PUT"
- 22.9 Reading Data from a Communication Partner within the Local S7 Station with SFC 72 "I_GET"
- 22.10 Aborting an Existing Connection to a Communication Partner within the Local S7 Station with SFC 74 " I_ ABORT"
- 23 Open Communication via Industrial Ethernet
- 23.1 Overview
- 23.2 Function of FBs for Open Communication via Industrial Ethernet
- 23.3 Assigning Parameters for Communications Connections with TCP native and ISO on TCP
- 23.4 Assigning Parameters for the Local Communications Access Point with UDP
- 23.5 Structure of the Address Information for the Remote Partner with UDP
- 23.6 Examples of Parameters for Communications Connections
- 23.7 Establishing a Connection with FB 65 "TCON"
- 23.8 Terminating a Connection with FB 66 "TDISCON"
- 23.9 Sending Data via TCP native and ISO on TCP with FB 63 " TSEND"
- 23.10 Receiving Data via TCP native and ISO on TCP with FB 64 " TRCV"
- 23.11 Sending Data via UDP with FB 67 "TUSEND"
- 23.12 Receiving Data via UDP with FB 68 "TURCV"
- 24 Generating Block-Related Messages
- 24.1 Introduction to Generating Block-Related Messages with SFBs
- 24.2 Generating Block-Related Messages without Acknowledgment with SFB 36 " NOTIFY"
- 24.3 Generating Block Related Messages without Acknowledgement Display with SFB 31 " NOTIFY_8P"
- 24.4 Generating Block-Related Messages with Acknowledgment with SFB 33 " ALARM"
- 24.5 Generating Block-Related Messages with Associated Values for Eight Signals with SFB 35 " ALARM_ 8P"
- 24.6 Generating Block-Related Messages without Associated Values for Eight Signals with SFB 34 " ALARM_ 8"
- 24.7 Sending Archive Data with SFB 37 "AR_SEND"
- 24.8 Disabling Block-Related, Symbol-Related and Group Status Messages with SFC 10 " DIS_ MSG"
- 24.9 Enabling Block-Related, Symbol-Related, and Group Status Messages with SFC 9 " EN_ MSG"
- 24.10 Startup Behavior of the SFBs for Generating Block- Related Messages
- 24.11 How the SFBs for Generating Block-Related Messages React to Problems
- 24.12 Introduction to Generating Block-Related Messages with SFCs
- 24.13 Generating Acknowledgeable Block-Related Messages with SFC 17 " ALARM_ SQ" and Permanently Acknowledged Block- Related Messages with SFC 18 " ALARM_ S"
- 24.14 Querying the Acknowledgment Status of the Last ALARM_ SQ/ ALARM_ DQ Entering Event Message with SFC 19 " ALARM_ SC"
- 24.15 Generating Acknowledgeable and Permanently Acknowledged Block Related Messages with SFCs 107 " ALARM_ DQ" and 108 " ALARM_ D"
- 24.16 Reading Dynamic System Resources with SFC 105 " READ_ SI"
- 24.17 Reading Dynamic System Resources with SFC 106 " DEL_ SI"
- 25 IEC Timers and IEC Counters
- 26 IEC Functions
- 26.1 Overview
- 26.2 Technical Data of the IEC Functions
- 26.3 Date and Time as Complex Data Types
- 26.4 Time-of-Day Functions
- 26.5 Comparing DATE_AND_TIME Variables
- 26.6 Comparing STRING Variables
- 26.7 Editing Number Values
- 26.8 Example in STL
- 26.9 Example in STL
- 26.10 Editing STRING Variables
- 26.11 Converting Data Type Formats
- 27 SFBs for Integrated Control
- 28 SFBs for Compact CPUs
- 28.1 Positioning With Analog Output Using SFB 44 " Analog"
- 28.2 Positioning with Digital Output Using SFB 46 " DIGITAL"
- 28.3 Controlling the Counter with SFB 47 "COUNT"
- 28.4 Controlling the Frequency Measurement with SFB 48 " FREQUENC"
- 28.5 Controlling Pulse Width Modulation with SFB 49 " PULSE"
- 28.6 Sending Data (ASCII, 3964(R)) with SFB 60 " SEND_ PTP"
- 28.7 Receiving Data (ASCII, 3964(R)) with SFB 61 " RCV_ PTP"
- 28.8 Deleting the Receive Buffer (ASCII, 3964(R)) with SFB 62 " RES_ RCVB"
- 28.9 Sending Data (512(R)) with SFB 63 "SEND_RK"
- 28.10 Fetching Data (RK 512) with SFB 64 "FETCH RK"
- 28.11 Receiving and Providing Data (RK 512) with SFB 65 " SERVE_ RK"
- 28.12 Additional Error Information of the SFBs 60 to 65
- 29 SFCs for H CPUs
- 30 Integrated Functions (for CPUs with integrated I/ Os)
- 31 Plastics Techology
- 32 Diagnostic Data
- 33 System Status Lists (SSL)
- 33.1 Overview of the System Status Lists (SSL)
- 33.2 Structure of a Partial SSL List
- 33.3 SSL-ID
- 33.4 Possible Partial System Status Lists
- 33.5 SSL-ID W#16#xy11 - Module Identification
- 33.6 SSL-ID W#16#xy12 - CPU Characteristics
- 33.7 SSL-ID W#16#xy13 - Memory Areas
- 33.8 SSL-ID W#16#xy14 - System Areas
- 33.9 SSL-ID W#16#xy15 - Block Types
- 33.10 SSL-ID W#16#xy19 - Status of the Module LEDs
- 33.11 SSL-ID W#16#xy1C - Component Identification
- 33.12 SSL-ID W#16#xy22 - Interrupt Status
- 33.13 SSL ID W#16#xy25 - Assignment of Process Image Partitions to OBs
- 33.14 SSL-ID W#16#xy32 - Communication Status Data
- 33.15 Data Record of the Partial List Extract with SSL-ID W# 16# 0132 Index W# 16# 0005
- 33.16 Data Record of the Partial List Extract with SSL-ID W# 16# 0132 Index W# 16# 0008
- 33.17 Data Record of the Partial List Extract with SSL-ID W# 16# 0132 Index W# 16# 000B
- 33.18 Data Record of the Partial List Extract with SSL-ID W# 16# 0132 Index W# 16# 000C
- 33.19 Data Record of the Partial List Extract with SSL-ID W# 16# 0232 Index W# 16# 0004
- 33.20 SSL-ID W#16#xy37 - Ethernet - Details of a Module
- 33.21 SSL-ID W#16#xy71 - H CPU Group Information
- 33.22 SSL-ID W#16#xy74 - Status of the Module LEDs
- 33.23 SSL-ID W#16#xy75 - Switched DP Slaves in the H System
- 33.24 SSL-ID W#16#xy90 - DP Master System Information
- 33.25 SSL-ID W#16#xy91 - Module Status Information
- 33.26 SSL-ID W#16#xy92 - Rack / Station Status Information
- 33.27 SSL-ID W#16#0x94 - Status Information for Rack/ Station
- 33.28 SSL-ID W#16#xy95 - Extended DP Master System Information
- 33.29 SSL-ID W#16#xy96 - PROFINET IO and PROFIBUS DP Module Status Information
- 33.30 SSL-ID W#16#xyA0 - Diagnostic Buffer
- 33.31 SSL-ID W#16#00B1 - Module Diagnostic Information
- 33.32 SSL-ID W#16#00B2 - Diagnostic Data Record 1 with Physical Address
- 33.33 SSL-ID W#16#00B3 - Module Diagnostic Data with Logical Base Address
- 33.34 SSL-ID W#16#00B4 - Diagnostic Data of a DP Slave
- 34 Events
- 34.1 Events and Event ID
- 34.2 Event Class 1 - Standard OB Events
- 34.3 Event Class 2 - Synchronous Errors
- 34.4 Event Class 3 - Asynchronous Errors
- 34.5 Event Class 4 - Stop Events and Other Mode Changes
- 34.6 Event Class 5 - Mode Run-time Events
- 34.7 Event Class 6 - Communication Events
- 34.8 Event Class 7 - H/F Events
- 34.9 Event Class 8 - Diagnostic Events for Modules
- 34.10 Event Class 9 - Standard User Events
- 34.11 Event Classes A and B - Free User Events
- 34.12 Reserved Event Classes
- 35 List of SFCs, and SFBs
- Bibliography
- Glossary
- Index
SFBs for Integrated Control
System Software for S7-300/400 System and Standard Functions - Volume 2/2
A5E00739858-01
27-17
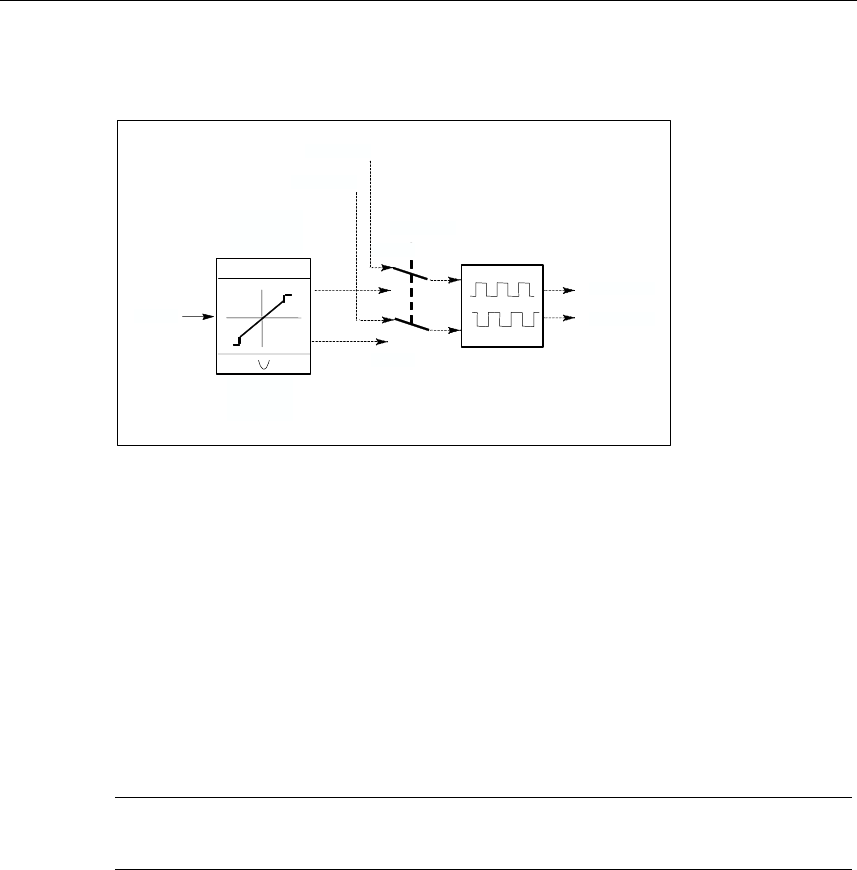
Block Diagram
#
QPOS_P
QNEG_P
MAN_ON
NEG_P_ON
POS_P_ON
INV
SYN_ON,
STEP3_ON,
ST2BI_ON
PER_TM,
P_B_TM,
RATIOFAC
0
1
Accuracy of the Manipulated Value
With a "sampling ratio" of 1:10 (CONT_C calls to PULSEGEN calls) the accuracy
of the manipulated value in this example is restricted to 10%, in other words, set
input values INV can only be simulated by a pulse duration at the QPOS output in
steps of 10 %.
The accuracy is increased as the number of SFB/FB "PULSEGEN" calls per
CONT_C call is increased.
If PULSEGEN is called, for example, 100 times more often than CONT_C, a
resolution of 1 % of the manipulated value range is achieved.
Note
The call frequency must be programmed by the user.
Automatic Synchronization
It is possible to synchronize the pulse output with the block that updates the input
variable INV (for example, CONT_C). This ensures that a change in the input
variable is output as quickly as possible as a pulse.
The pulse generator evaluates the input value INV at intervals corresponding to the
period PER_TM and converts the value into a pulse signal of corresponding length.
Since, however, INV is usually calculated in a slower cyclic interrupt class, the
pulse generator should start the conversion of the discrete value into a pulse signal
as soon as possible after the updating of INV.
To allow this, the block can synchronize the start of the period using the following
procedure:










