4.4 ROU (Remote Optic Unit) ROU receives TX optical signals from ODU or OEU and converts them into RF signals. The converted RF signals are amplified through High Power Amp in a corresponding RDU, combined with Multiplexer module and then radiated to the antenna port. When receiving RX signals through the antenna port, this unit filters out-of-band signals in a corresponding RDU and sends the results to Remote Optic Module to make electronic-optical conversion of them.
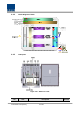
4.4.2 Block Diagram of ROU 4.4.3 ROU parts Figure 4.26 – ROU Inner Look No.
Remote Drive Unit Filter and high amplify TX signals; 1 RDU+BPF Filter and amplify RX signals; Remove other signals through BPF BPF is exclude from VHF+UHF module Remote Power Supply Unit 2 RPSU Input power: DC -48V, Output power: 27V,9V, 6V For 120V input of AC/DC; For -48V input of DC/DC Remote Optic Make RF conversion of TX optical signals; 3 R-OPTIC Convert RX RF signals into optical signals; Compensates optical loss Communicates with BIU/OEU though the FSK modem Remote Central Processor Unit 4
.4.4 1) Function by unit Remote Drive Unit (RDU) When receiving TX signals from each band through Remote Optic, RDU filters the signals and amplifies them with High Power Ampifier. The unit also filters RX signals given through Multiplexer and amplifies them to send the signals to Remote Optic. In the unit, there is ATT to adjust gain.
850C VHF+UHF 850C+700PS 1900P+AWS-1 850C+700LTEC Figure 4.27 – RDU Outer Look 2) Remote Power Supply Unit (RPSU) RPSU receives -48V of input. This unit is divided into DC/DC type to output +6V, +9V and +27V of DC power and AC/DC type to receive 120V of AC input and to output +6V, +9V and +27V of DC power. Upon order, either of the two types should be decided.
receive inputs, is designed to accept any of AC and DC. Only in this case, the input cable is different. RPSU has a circuit brake to turn the power ON/OFF and has LED indicator at the top to check if input power is normally supplied. 3) Remote Optic(R OPTIC) Remote Optic converts optical signals into RF signals and performs vice versa. With an FSK modem in it, the unit communicates with upper devices. It also has internal ATT for optical compensation to compensate for optical cable loss, if any. Figure 4.
communication data from Remote Optic and reports the unit's own value to upper devices. At the front of the module, it has LED indicator to show system status, letting you check any abnormalities at a time. At the same front, it also has communication LED Indicators to show communication status with upper devices. Through RS-232C Serial Port, the unit enables you to check and control device status through PC and laptop.
Figure 4.30 – Multiplexer Outer Look 6) System Interface Unit(SIU) SIU distributes power and signals to each module.
4.4.5 Bottom of ROU 1) Functions Figure 4.
Item Description 1. VHF/UHF TX/RX Port Terminal for TX and RX antenna ports of VHF and UHF 2.Antenna Port System Antenna Port, N-type female 3. Power Port AC 120V input port or DC-48V input port 4. Optic Port Optical input port 5.External Port Port for external devices 6.
4.5 Add on V/UHF ROU Add on V/UHF ROU(forward naming“AOR) is connected existing ROU to service VHF and UHF band. AOR should support VHF+UHF RDU only, not support other RDUs which have cavity filter. RDUs which have cavity filter is too big so that AOR body can’t accommodate these. AOR locates above or under of exisiting ROU. AOR receives TX signals from ROU and then amplify these through High Power Amplifier, filter out of band signals and radiated to the TX antenna port.
4.5.2 Block Diagram of AOR 4.5.3 AOR parts Figure 4.33 – AOR Inner Look No.
AOR Power Supply Unit 2 AOR PSU Input power: DC -48V, Output power: 27V,9V, 6V For 110V input of AC/DC; For -48V input of DC/DC 3 Enclosure 4 SIU 4.5.4 Enclosure to satisfy NEMA4; Enable both Wall and Rack Mount; System Interface Unit Distribute power and signals of module Function by unit 1) VHF+UHF Remote Drive Unit (RDU) When receiving TX signals from each band through existing ROU’s Remote Optic, RDU filters out of band signals and amplifies them with High Power Ampifier.
+27V of DC power. Upon your order, either of the two types should be decided. MS Connector, which uses ports to receive inputs, is designed to accept any of AC and DC. Only in this case, the input cable is different. RPSU has a circuit brake to turn the power ON/OFF and has LED indicator at the top to check if output power is normally supplied. 3) AOR System Interface Unit(SIU) SIU distributes power and signals to each module. 4.5.
Figure 4.35 – AOR Rear Look Item Description 1. VHF/UHF TX IN Terminal for receive the signal of TX from existing ROU 2. VHF/UHF RX OUT Terminal for transmit the signal of RX to existing ROU Remark To/From Existing 3. Power Port ROU Terminal for input either AC 110V or DC-48V as internal PSU type 4. VHF/UHF TX IN Terminal for radiate the signal of TX to TX Antenna 5. VHF/UHF RX OUT Terminal for receive the signal of RX from RX Antenna 5.
Exteral PORT External ports are reserved ports for external equipments for future implementation, and used to monitor the status and control the equipments. Below figure is naming of the external ports.
Section5 System Installation & Operation 5.1 BIU Installation 5.2 ODU Installation 5.3 ROU Installation 5.4 OEU Installation 5.5 System Operation and Alarm Status 5.
This chapter describes how to install each unit and optical cables, along with power cabling method. In detail, the chapter describes how to install shelves or enclosuers of each unit, Power Cabling method and Optic Cabling and RF Interface. Furthermore, by showing power consumption of modules to be installed in each unit, it presents Power Cabling budget in a simple way. Then, it describes the quantity of components of modules to be installed in each unit and expansion method. 5.1 BIU Installation 5.1.
Basically, the common part of BIU should have shelves and it should be equipped with MCDU to combine and divide TX/RX signals, MPSU to supply devices with power, MCPU to inquire and control state of each module and Power Cable to supply power from external rectifiers. In addition, MDBU can be inserted and removed to provide services for desired band (Optional). 5.1.2 BIU Power Cabling BIU has -48V of input power. This unit should connect DC cable with the Terminal Block seen at the rear of BIU.
Note that BIU does not operate if the "+" terminal and the "–" terminal of the -48V power are not inserted into the accurate polarity. When you connect -48V power with BIU, use the ON/OFF switch of MPSU located at the front of BIU to check the power.
5.1.3 RF Interface at BIU BIU can be connected with Bi-Directional Amplifier and Base Station Tranceiver. To connect BIU with BDA, you need to use a duplexer or a circulator to separate TX/RX signals from each other. BIU can feed external TX/RX signals from the Back Plane. Using MDBU separated from each carrier band, BIU can easily expand and interface with bands. As seen in the table below, MDBU is divided into Single and Dual Bands. The unit can be connected with two to four carrier signals per band.
AWS-1 AWS-1 TX(2110~2155MHz) RX(1710~1755MHz) AWS-1 AWS-1 TX(2110~2155MHz) RX(1710~1755MHz) AWS-1 AWS-1 TX(2110~2155MHz) RX(1710~1755MHz) 800PS 800PS TX(851~869MHz) RX(806~869MHz) 800PS 800PS TX(851~869MHz) RX(806~869MHz) Paging Paging TX(929~932MHz) RX(896~902MHz) 900I TX(929~941MHz) 900I RX(896~902MHz) 700PS 700PS TX(764~776MHz) RX(794~806MHz) 700PS 700PS TX(764~776MHz) RX(794~806MHz) Port#3 850C TX(869~894MHz) 850C RX(824~849MHz) Port#4 850C TX(869~894MHz) 850C RX(8
For each port, TX signals and RX signals are separated from each other. You don't have to terminate unused ports unless you want to. BIU interface with Base station Transceiver Basically, BIU has different TX and RX ports, and so, you have only to connect input and output ports. Through spectrum, you need to check signals sent from BTS TX. If the signals exceed input range (-20dBm~+10dBm), you can connect an attenuator ahead of the input port to put the signals in the input range.
from each other. Figure 5.2 – 800PS BDA Interface using Circulator Figure 5.3 – 800PS BDA Interface using Duplexer BIU interfaces with BDA in either of the methods above. In this case, you need to check TX input range as well.
Given the TX input range (-20dBm~+10dBm/Total per port), make sure to see if the value is in the input range, using Spectrum Analyzer, when you connect input ports. 5.1.4 MDBU insertion MDBU is designed to let a MDBU be inserted into any slot. BIU can be equipped with a total of four MDBUs. If only one MDBU is inserted into a slot with the other slots reserved, you need to insert BLANK cards into the other slots.
If you do not terminate input and output ports of MCDU, which combines TX signals and divides RX signals, it will cause loss and generation of spurious signals at the other party's band. Given this, make sure to insert MDBU BLANK into slots of MDBU.
LED Description Power is not supplied. ON Power is supplied. Normal Operation ALM Abnormal Operation MONITOR SMA port seen at the front panel of MDBU enables you to check current level of TX input and RX output signals in current service without affecting main signals. TX MON is -20dB compared with TX Input power and RX MON is -20dB as well compared with RX Output power. 5.1.5 ODU Interface BIU supports up to four ODUs.
At the rear part of ODU, the number of RF Ports and Signal Ports are printed in order. Therefore, you need to be careful in case of expansion of ODU.
If ODU is not connected in the right order, related devices may fail to communicate with each other or the unit may read wrong information. Given this, you need to connect the unit with accurate RF Port and Signal Port in a corresponding number.
For unused RF Ports for ODU expansion, make sure to terminate them using SMA Term.
When you put ODU on the top of BIU, it is recommended to install the unit at least 1U apart from BIU. Heat from BIU climbes up to reach ODU. 5.1.6 Consumption Power of BIU The table below shows power consumption of BIU: Part Common Part Unit Consumption Power Shelf 7.
MCPU MPSU MDBU MDBU 800PS 12W MDBU 800PS+900I+Paging 20W MDBU 850C 12W MDBU 850C+700PS 19W MDBU 1900P 20W MDBU AWS-1 12W MDBU 850C+700LTEC 19W BIU supplies power for ODU. Therefore, when you want to calculate total power consumption of BIU, you need to add power consumption of ODU to the total value. Power consumption of ODU is given in the later paragraph describing ODU. 5.2 ODU Installation ODU should be, in any case, put on the top of BIU.
front panel is lit. Through this LED, you can check state values of LD and PD of DOU. 5.2.3 ODU Optic Cabling As optical module shelf, ODU makes electronic-optical conversion of TX signals and then makes optical-electronic conversion of RX signals. ODU can be equipped with up to two DOUs. One DOU supports four optical ports and one optical port can be connected with ROU. Optionally, only optical port 4 can be connected with OEU.
When you insert DOU into ODU, insert the unit into the left DOU1 slot first. Into unused slot, you need to insert BLANK UNIT in any case. 5.2.5 Consumption Power of ODU ODU gets power from BIU. One ODU can be equipped with up to two DOUs. Depending on how many DOUs are installed, power consumption varies.
consumption of ODU: Part Unit Consumption Power ODU_4 DOU 1 EA 13W ODU_8 DOU 2 EA 26W 5.3 5.3.1 Remark ROU Installation ROU Enclosure installation ROU is designed to be water- and dirt-proof. The unit has the structure of One-Body enclosure. It satisfies water-proof and quake-proof standards equivalent of NEMA4. ROU can be mounted into either of a 19” Standard Rack or on a Wall. Basically, ROU has both of a Wall Mount Bracket and a Rack Mount Bracket.