user manual
Table Of Contents
- Introduction
- Optimizing for Sound Forge
- Learning the Sound Forge Workspace
- Getting Started
- Navigating, Zooming, and Selecting
- Changing File Attributes and Formats
- Using Markers, Regions, and the Playlist/Cutlist
- Why use markers, regions, and the playlist?
- Using markers
- Using command markers in streaming media files
- Using regions
- Using the Regions List
- Using the playlist
- Displaying the playlist
- Adding regions to the playlist
- Understanding the playlist display
- Customizing the playlist display
- Repeating a region during playlist playback
- Playing from the playlist
- Arranging the playlist
- Replicating a region in the playlist
- Using stop points
- Deleting a region from the playlist
- Creating a new file from the playlist
- Configuring the playlist as a cutlist
- Saving a playlist/cutlist file
- Opening a playlist/cutlist file
- Copying the playlist/cutlist to the clipboard
- Recording, Extracting, and Burning
- Recording audio
- Recording manually
- Recording automatically
- Recording a specific length (punch-in)
- Choosing a recording mode
- Adjusting for DC offset
- Playing back recorded audio
- Using remote recording mode
- Synchronizing with other devices
- Viewing input levels
- Inserting markers while recording
- Configuring gap detection
- Automatically labeling windows and regions
- Changing blinking status
- Extracting audio from CDs
- Burning CDs
- Proper use of software
- Recording audio
- Editing, Repairing, and Synthesizing Audio
- Processing Audio
- Applying Effects
- Adding an effect
- Adding a chain of effects
- Applying effects using the Plug-In Chainer
- Adding plug-ins to a chain
- Selecting the processing mode for audio tail data
- Arranging plug-ins on a chain
- Bypassing effects
- Removing plug-ins from a chain
- Configuring chained plug-ins
- Saving individual plug-in settings as a custom preset
- Saving plug-in chains
- Loading plug-in chains
- Managing effects
- Automating Effect Parameters
- Adjusting envelopes
- Using Acoustic Mirror and Wave Hammer
- Working with MIDI/SMPTE
- Sampling
- Looping
- Working with Video
- Using Spectrum Analysis
- Working in the frequency domain
- Using a spectrum graph
- Displaying a spectrum graph
- Monitoring an input and output source
- Displaying frequency and amplitude values, notes and statistics
- Navigating a spectrum graph
- Changing the graph type
- Changing the zoom level
- Working with stereo files
- Updating a spectrum graph
- Viewing multiple spectrum graphs
- Creating and comparing snapshots of the Spectrum Analysis window
- Printing the graph
- Using a sonogram
- Adjusting Spectrum Analysis settings
- Shortcuts
- Microsoft Audio Compression Manager
- SMPTE Timecode
- Using CSOUND, MTU, IRCAM, BICSF, and EBICSF Files
- Index
52
GETTING STARTED CHP. 4
Viewing selection statistics
Choosing Statistics from the Tools menu displays a Statistics dialog showing information about the current
selection or, if there is no selection, on the entire file. The following table describes all statistical categories
displayed in the Statistics dialog.
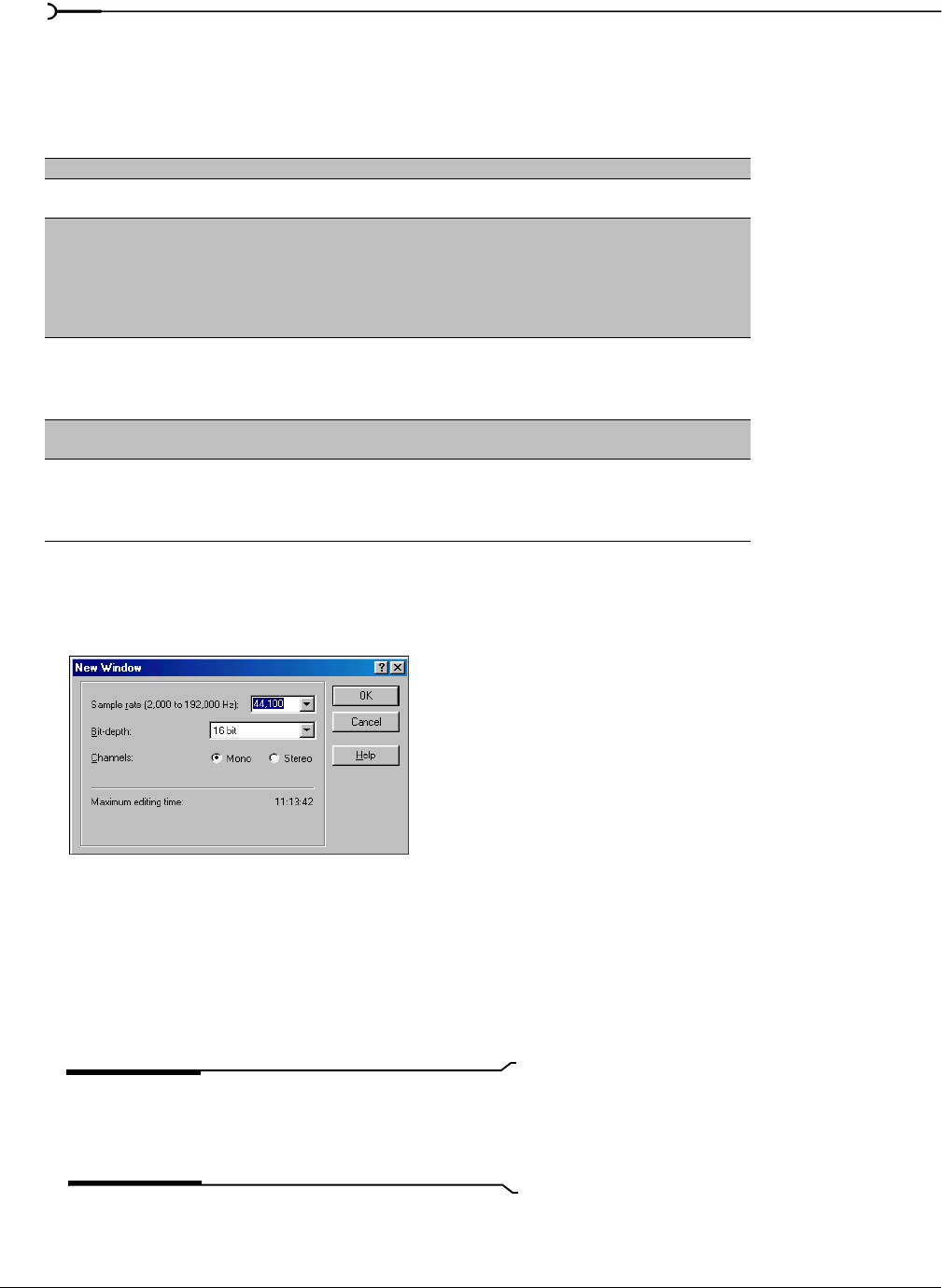
Creating a new data window
1.
From the File menu, choose New. The New Window dialog appears.
2.
Complete the New Window dialog:
• From the
Sample rate drop-down list, choose a sample rate.
• From the
Bit-depth drop-down list, choose a bit depth.
• Select the desired
Channels radio button.
For more information, see Editing file attributes on page 83.
3.
Click OK. A new data window with the specified attributes appears.
Tip:
Sound Forge automatically names new windows. You
can customize this automatic naming feature to suit your
needs. For more information, see Customizing automatic
labeling on page 93.
Cursor position The cursor position (in samples) from the start of the audio file.
Sample value at cursor The actual number stored by a single sample. The maximum allowed sample value is
often referred to as 100% or 0 dB.
Maximum/minimum
sample position and
sample value
The maximum and minimum sample values and the locations (in samples) where they
occur.
These values may help determine if clipping will occur in the audio file. These values can
also be used to determine the noise level of a signal for use with Noise Gate (a built-in
XFX plug-in installed with the full version of Sound Forge). For example, to determine
the noise amplitude of a file, run Statistics on a region of noisy silence.
RMS power The Root Mean Square of the sample values relative to the RMS value of a maximum-
amplitude square wave (the loudest possible recording).
On short intervals, this value relates to the volume level of the audio file. If used on a
large selection with large volume variation, this value becomes less meaningful.
Average value (DC Offset) The sum of all sample values in the selected region divided by the number of samples. If
this value is not zero, it usually indicates a DC offset in the recording process.
Zero crossings The number of times per second that the waveform fluctuates from a negative to a
positive value.
This value can be used as a rough estimate of the frequency of the audio data for very
simple waveforms.
New Window dialog